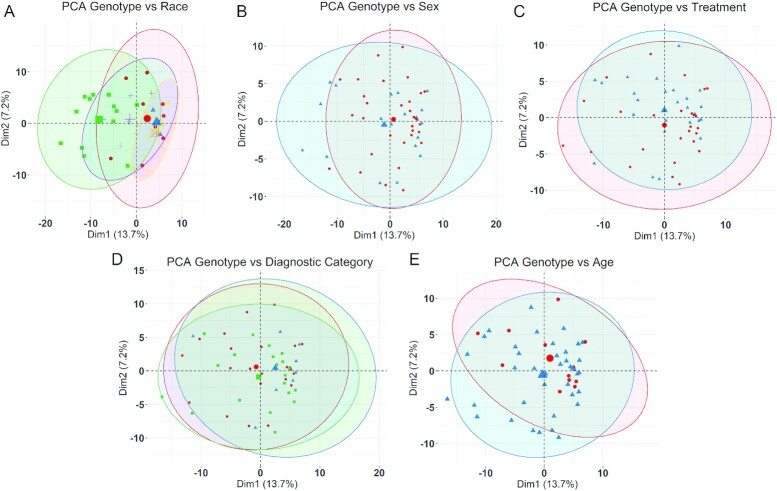
FIGURE 2.
PCA of genotypes and population characteristics. PCA (FactoMineR, v2.3) was used to examine the genomic separation of all 52 participants based on race, sex, treatment, diagnostic category, or age. No significant associations between genotype and any of these population characteristics were observed in the PCA. (A) Self-identified race vs. genotype. Red circles, Native American (n = 10); blue triangles, Asian (n = 2); green squares, Black or African-American (n = 13); purple crosses, multiracial (n = 7); yellow crossed squares, White or Caucasian (n = 19); orange crossed squares, unknown (n = 1). (B) Sex vs. genotype. Red circles, female (n = 33); blue triangles, male (n = 19). (C) Treatment vs. genotype. Red circles, choline-treated (n = 26); blue triangles, placebo-treated (n = 26). (D) Diagnostic category vs. genotype. Red circles, alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorder (n = 23); blue triangles, FAS (n = 9); green squares, partial FAS (n = 20). (E) Age vs. genotype. Red circles, 3 y or younger (n = 12); blue triangles, older than 3 y (n = 40). The largest symbol for each population characteristic represents the group mean for that characteristic, and the ellipse is the 95% CI surrounding that group mean. Dim1, dimension1; Dim2, dimension 2; FAS, fetal alcohol syndrome; PCA, principal components analysis.