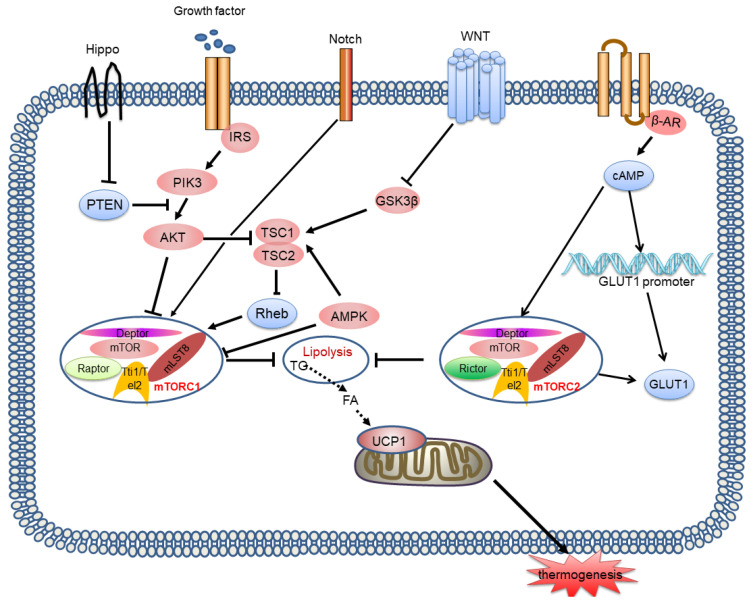
Figure 4.
mTORC1 and mTORC2 signalling pathways and their signalling networks. The mTORC1 and mTORC2 signalling pathways are involved in thermogenesis by inhibiting lipolysis and regulating thermogenic gene expression. Growth factors activates the PI3K-AKT-TSC2-mTORC1 pathway. Wnt signalling inhibits the activation of GSK3β, which phosphorylates TSC2, resulting in mTORC1 stimulation. Notch signalling also affects mTOR activity. AMPK phosphorylates TSC2 resulting in inhibition of mTORC1 activity. Hippo activates mTORC1 signalling through PTEN suppression. mTORC2 is also involved in controlling glucose homeostasis. mTORC2 is stimulated by β-AR and then activates glucose metabolism and lipid oxidation, which is associated with thermogenesis. mTORC2 stimulates GLUT1 transport to the plasma membrane and increases glucose uptake. mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; GSK3β: glycogen synthase kinase 3β; TSC2: tuberous sclerosis complex 2; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homologue; GLUT1: glucose trans porter-1