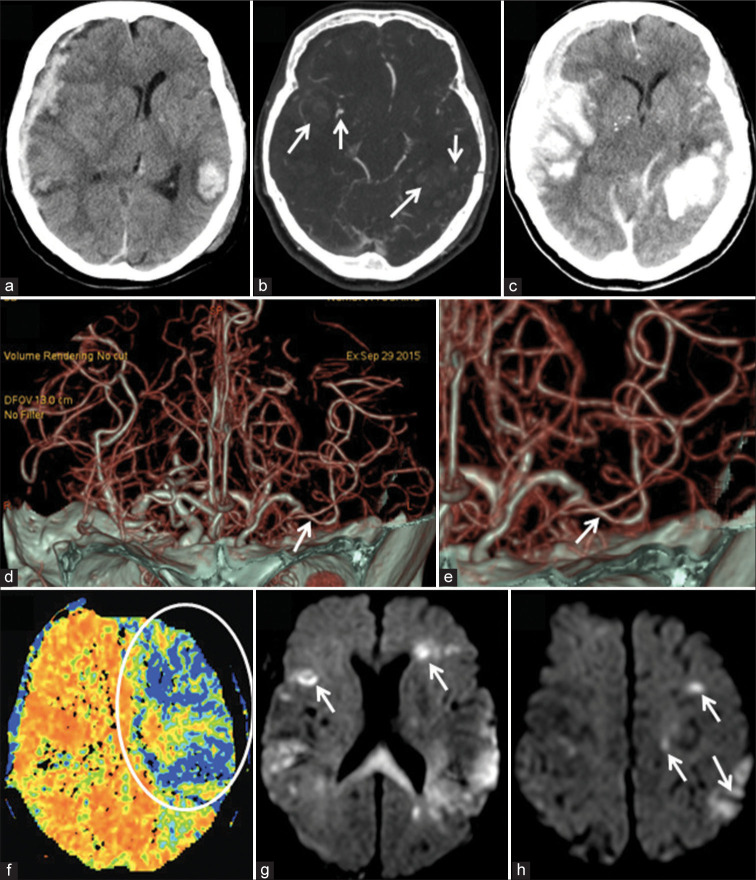
Figure 1:
Neuroimaging findings in a 77-year-old woman with traumatic brain injury. Plain head CT at admission (a) revealed acute subdural hematoma above the right cerebral convexity causing brain shift, as well as multiple brain contusions, intracerebral hemorrhages, and subarachnoid hemorrhage, whereas CT angiography (CTA) (b) defined spot signs (arrows) within the anterior right temporal and posterior left temporal lobes. One hour later prominent expansion of the intracerebral hemorrhages was noted (c), thus urgent right-sided decompressive craniectomy and the evacuation of subdural hematoma were done. On the 8th day after trauma and surgery, CTA (d and e) revealed localized vasospasm of the left M2 segment (arrows), whereas CT perfusion (f) showed marked hypoperfusion of the left frontal and temporal lobes (circle). Subsequent diffusion-weighted imaging (g and h) demonstrated multiple ischemic lesions (arrows) in both hemispheres.