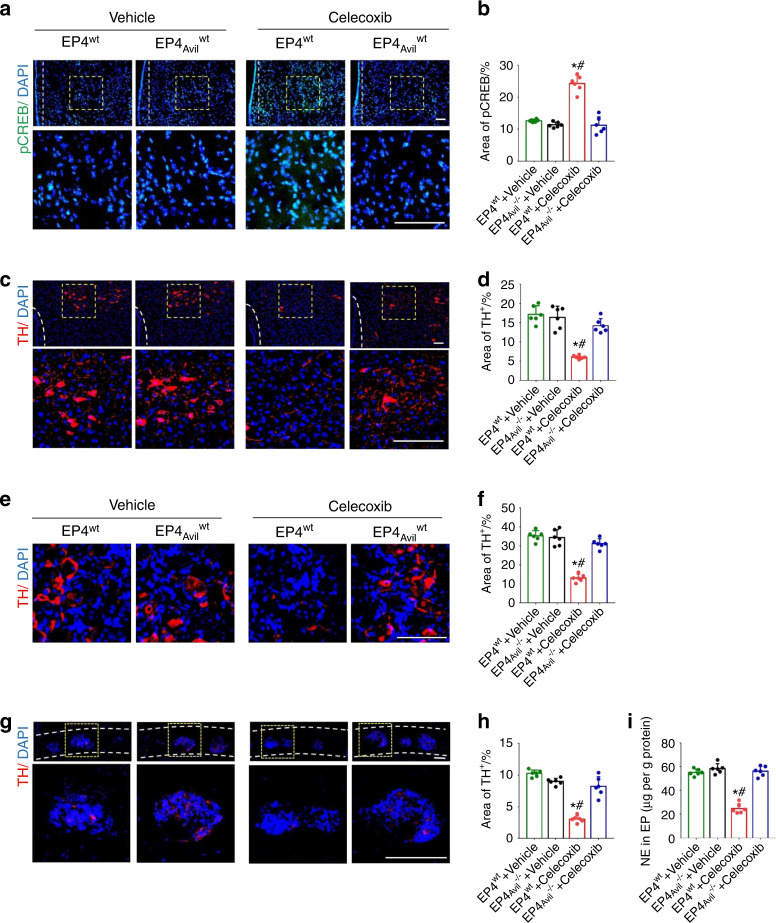
Fig. 6.
Knockout of the EP4 receptor in the sensory nerves influenced the effect of low-dose celecoxib on pCREB expression in the VMH and TH expression in the PVN, cervicothoracic ganglion and endplate. a Representative images of immunostaining of pCREB (green) and DAPI (blue) in hypothalamic VMH in the EP4wt or EP4Avil−/− mice at 2 weeks after celecoxib or vehicle treatment. b Quantitative analysis of the pCREB+ area in the VMH. c Representative images of immunostaining of TH (red) and DAPI (blue) in the hypothalamic PVN in the EP4wt or EP4Avil−/− mice at 2 weeks after celecoxib or vehicle treatment. d Quantitative analysis of the TH+ area in the PVN. e Representative images of immunostaining of TH (red) and DAPI (blue) in the cervicothoracic ganglion of the EP4wt or EP4Avil−/− mice at 2 weeks after celecoxib or vehicle treatment. f Quantitative analysis of the TH+ area in the cervicothoracic ganglion. g Representative images of immunostaining of TH (red) and DAPI (blue) in the endplates of the EP4wt or EP4Avil−/− mice at 2 weeks after celecoxib or vehicle treatment. h Quantitative analysis of the TH+ area in endplates. i ELISAs of norepinephrine concentration in lumbar endplates in the EP4wt or EP4Avil−/− mice at 2 weeks after celecoxib or vehicle treatment. Scale bars, 50 μm (a, c, e, g). *P < 0.05 compared with the sham group and #P < 0.05 compared with the vehicle group at the corresponding time points. n = 6 per group (b, d, f, h, i)