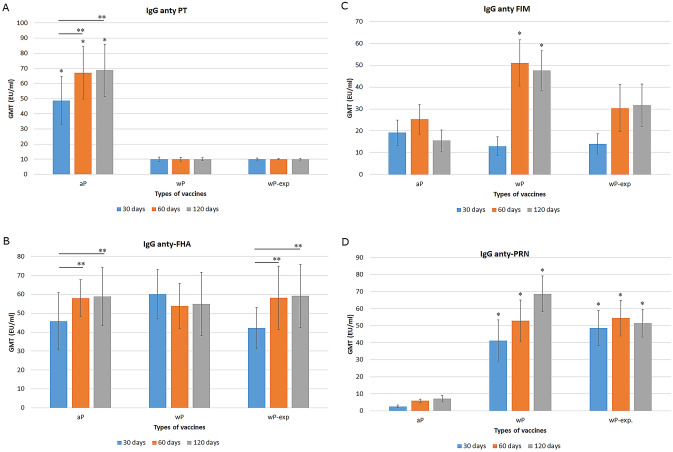
Fig. 1.
Distribution of pertussis toxin antibodies (A), filamentous hemagglutinin adhesion antibodies (B), fimbriae antibodies (C), pertactin antibodies (D) after immunisation of different types of B.pertussis vaccines. Results are shown as geometric mean titres (EU) per ml plus SD. ANOVA followed by Sheffe’s multiple comparison test was used to analyse the statistical significance between groups. Only significant differences are indicated * or * * (p < 0.05). * differences between different types of vaccines. ** differences between immunisation time. A * aP vaccine was induce significantly higher level of IgG anti-PT than wP vaccines used at any time tested after immunisation. ** Levels of IgG anti-PT increased significantly 60 and 120 days after immunisation compared to 30 days after immunisation. B ** From aP and wP-exp vaccines, the level of IgG anti-FHA antibodies increased significantly at 60 and 120 days after immunisation compared to the day 30. C * Commercial wP vaccine induced significantly higher levels of IgG anti-FIM antibodies at 60 and 120 days after immunisation compared to the other tested vaccines. D * IgG anti-PRN were induced at a significantly higher level by both whole-cell pertussis vaccines used than the acellular vaccine at the three time points analysed