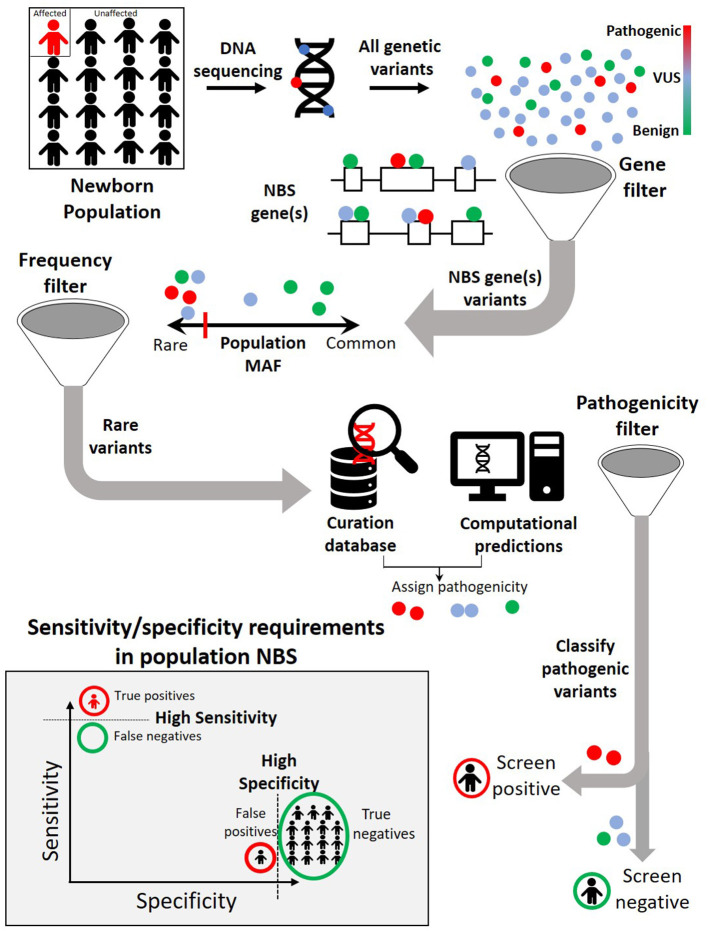
Figure 2.
A typical genomic analysis pipeline in the context of newborn screening (NBS). Among all the variants observed in the newborn DNA sequence, only those occurring in previously identified NBS genes are considered further. Within NBS genes, rare variants are prioritized over common variants. A combination of curated pathogenic variant databases and computational prediction tools is utilized to assign variant pathogenicity and screen for individuals who carry such variants. For NBS, the pipeline will need to demonstrate both a high sensitivity (screen positive almost all newborns with disease) and a high specificity (screen negative almost all newborns without disease).