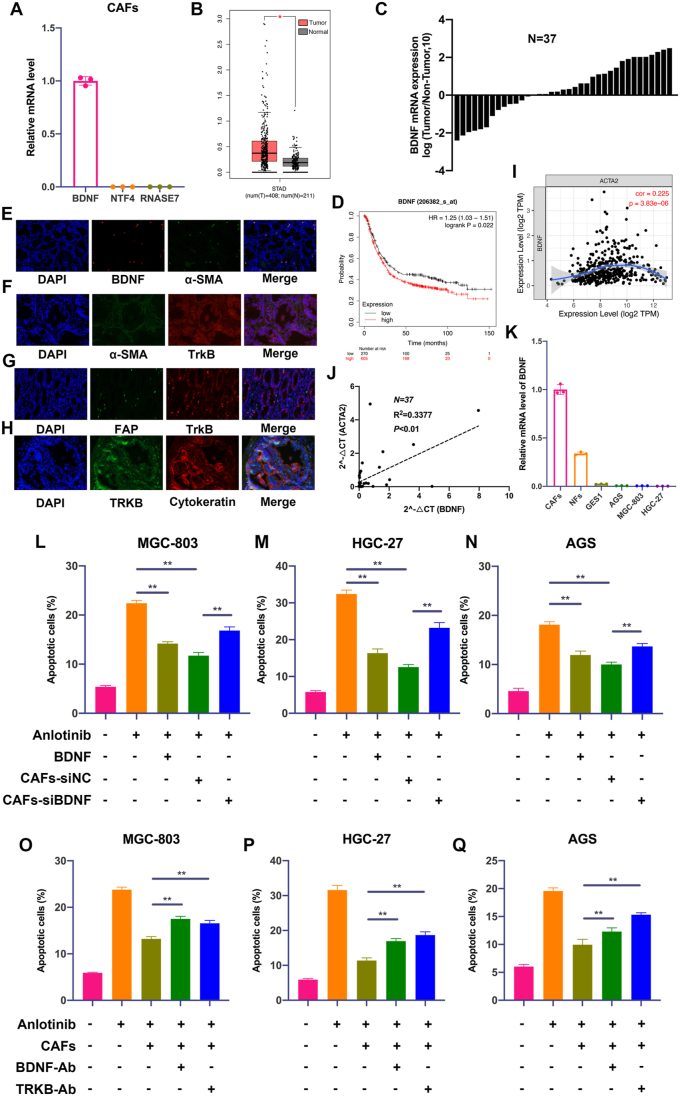
Fig. 5.
CAFs-derived BDNF protects GC cells from anlotinib-induced apoptosis. A. The mRNA levels of BDNF, NTF4 and RNASE7 were detected by qRT-PCR in CAFs. B. The mRNA level of BDNF in GC samples and normal samples from TCGA data. C. QRT-PCR analysis of BDNF mRNA expression in GC tumor tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues (n = 37). D. The overall survival analyses were plotted using Kaplan-Meier Plotter for GC patients with low or high levels of BDNF. E. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) staining of α-SMA and BDNF in GC tissues (200 × ). F–H. Immunofluorescence (IF) staining of BDNF, α-SMA, FAP, TrkB and Cytokeratin in GC tissues (200 × ). I. Correlation analysis of BDNF and α-SMA via TCGA data. J. Correlation analysis of the mRNA expression of BDNF and α-SMA in 37 pairs of GC tissues (Ruijin cohort). K. The mRNA expression of BNDF in CAFs, NFs, GES-1 and GC cell lines. L-N. Apoptosis of GC cells was detected after treatment with anlotinib (5 μM), exogenous BDNF or co-culture with CAFs transfected with BDNF/siRNA or NC/siRNA. O-Q. Apoptosis of GC cells was detected after treatment with anlotinib (5 μM), and/or co-culture with CAFs in the presence of IgG isotype antibody, BDNF neutralizing antibody or TrkB neutralizing antibody. Data are represented as the mean ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.