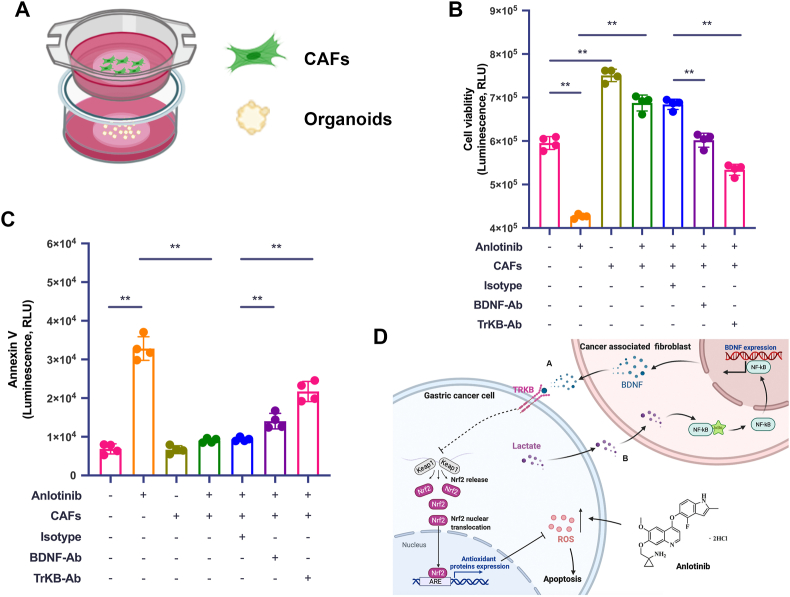
Fig. 8.
Blocking BDNF/TrkB pathway inhibits CAFs-induced protection of GC cells from anlotinib in human PDO model. A. Schematic illustration of the co-culture platform. B. Viability assay of PDO after indicated treatments for 72 h, detected by CellTiter-Glo 3D Cell Viability Assay. C. Apoptosis assay of PDO after indicated treatments for 72 h, monitored by RT-Glo Annexin V. D. Model for the epithelial-stromal interactions in the tumor microenvironment that induces anlotinib resistance in human GC. a. BDNF released from CAFs reduces anlotini-induced ROS and apoptosis of GC cells via the TrkB/Keap1-Nrf2 pathway, resulting in GC cells resistance to anlotinib. b. GC cell-derived lactate upregulates BDNF expression in CAFs via the NF-κB pathway. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).