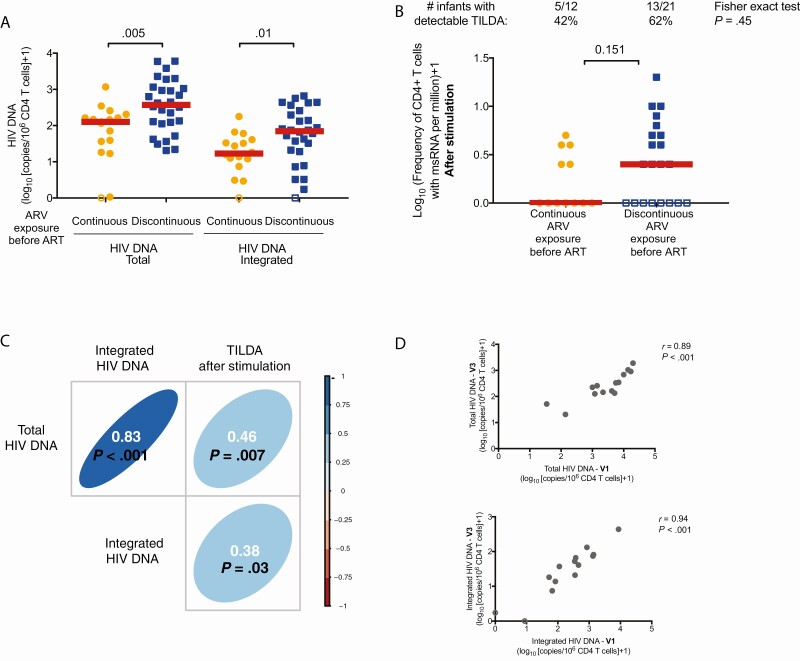
Figure 2.
Markers of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) persistence in infants after 1 year of antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation in the RV475/HIVNAT209 study, visit 3 (n = 45). Infants were subgrouped according to their prophylactic history: continuous antiretroviral (ARV) exposure since birth (direct transition from ARV prophylaxis to ART, orange circles, n = 17) vs discontinuous ARV exposure before ART initiation (blue squares, n = 28). A, Frequency of total and integrated HIV DNA in enriched CD4+ T cells. P values were obtained from Mann-Whitney U test. B, Frequency of cells producing multiply spliced RNA (msRNA) after stimulation (inducible reservoir) in enriched CD4+ T cells. Since > 15% of the samples were below the limit of detection, Tat/rev induced limiting dilution assay (TILDA) measurements were considered as categorical values (detectable vs undetectable). The numbers of samples (and corresponding percentages) in which msRNA was detected are indicated. P values were obtained from Fisher exact test. C, Correlation matrix between markers of HIV persistence at visit 3. D, Correlation between the frequency of total and integrated HIV DNA at visit 1 and visit 3. C and D, P values were obtained from the Spearman correlation test. In all panels, samples below the limit of detection of the assay (which varies according to the number of cells analyzed) were considered as 0 for statistical analysis and are indicated as open circles in all graphs.