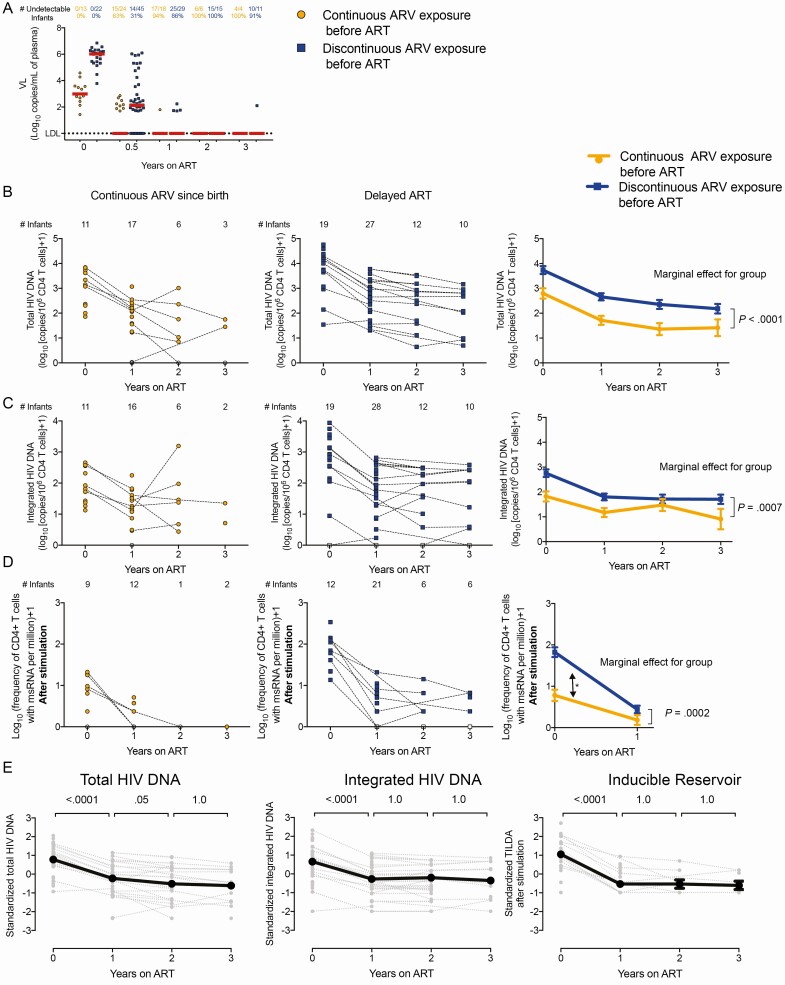
Figure 3.
Longitudinal analysis of markers of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) persistence in the RV475/HIVNAT209 study (n = 85). Infants were subgrouped according to their prophylactic history: continuous antiretroviral (ARV) exposure since birth (direct transition from prophylactic ARVs to antiretroviral therapy [ART], orange circles, n = 34) vs discontinuous ARV exposure before ART initiation (blue squares, n = 51). Samples collected immediately prior to ART initiation (time point 0) were included. Participants were followed for 3 years on ART. A, Plasma viral loads (VLs). The numbers of samples in which HIV RNA in plasma were detected (and the corresponding percentages) are indicated for each group. B–D, Levels of total (B) and integrated (C) HIV DNA, and frequencies of cells expressing multiply spliced RNA after stimulation (Tat/rev induced limiting dilution assay after stimulation, D) in enriched CD4+ T cells from infants who received continuous ARV since birth (left panels, in orange) and those who discontinued prophylactic treatment before ART initiation (middle panels, in blue). The numbers of samples tested at each time point are indicated. Right panels show the estimated means and standard errors, using a linear mixed model with the group of prophylaxis (continuous vs discontinuous ARV exposure before ART), visits (V1, V3, V5 and V7), and the interaction group × visit as independent variables. Participant identifier was used as a random variable, to take into account the within-children correlation. Because the interaction was not significant, the additive model was used as the final model with visit and group of prophylaxis as independent variables (no interaction included). For each model, the P value associated to the marginal effect for the group is indicated. E, HIV persistence markers were standardized to compare the decay rates. P values reported are Bonferroni-adjusted and calculated from pairwise post hoc comparisons between visits. The model used was similarly the additive mixed model with the group of prophylaxis, with the visit (V1–V7) as fixed effect and participant identifier as random effect.