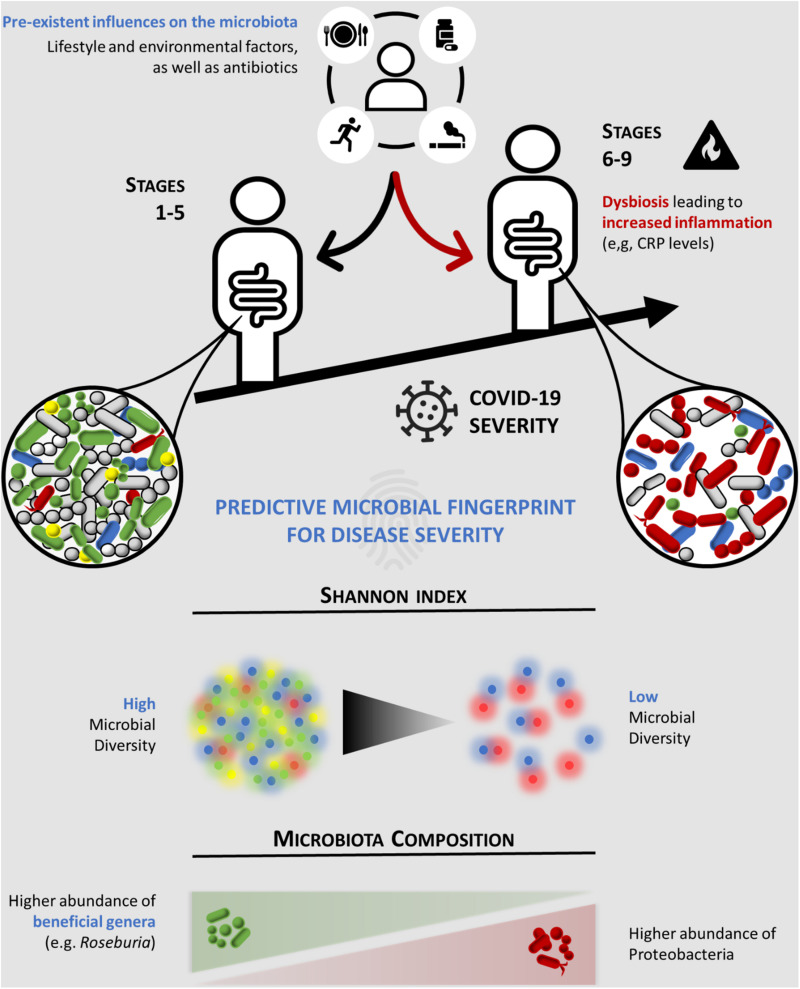
FIGURE 4.
Schematic representation of the predictive microbial fingerprint for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity. Preexistent influences on the microbiota, such as lifestyle and environmental factors, and antibiotics can induce dysbiosis (red arrow), leading to increased inflammation (e.g., CRP levels). Hence, lower overall microbial diversity and abundance of beneficial commensal microorganisms (e.g., Roseburia), along with an increased abundance of Proteobacteria, are associated with high COVID-19 severity (a score of ≥ 6 in the WHO Clinical Progression Scale). CRP, C-reactive protein.