Figure 1.
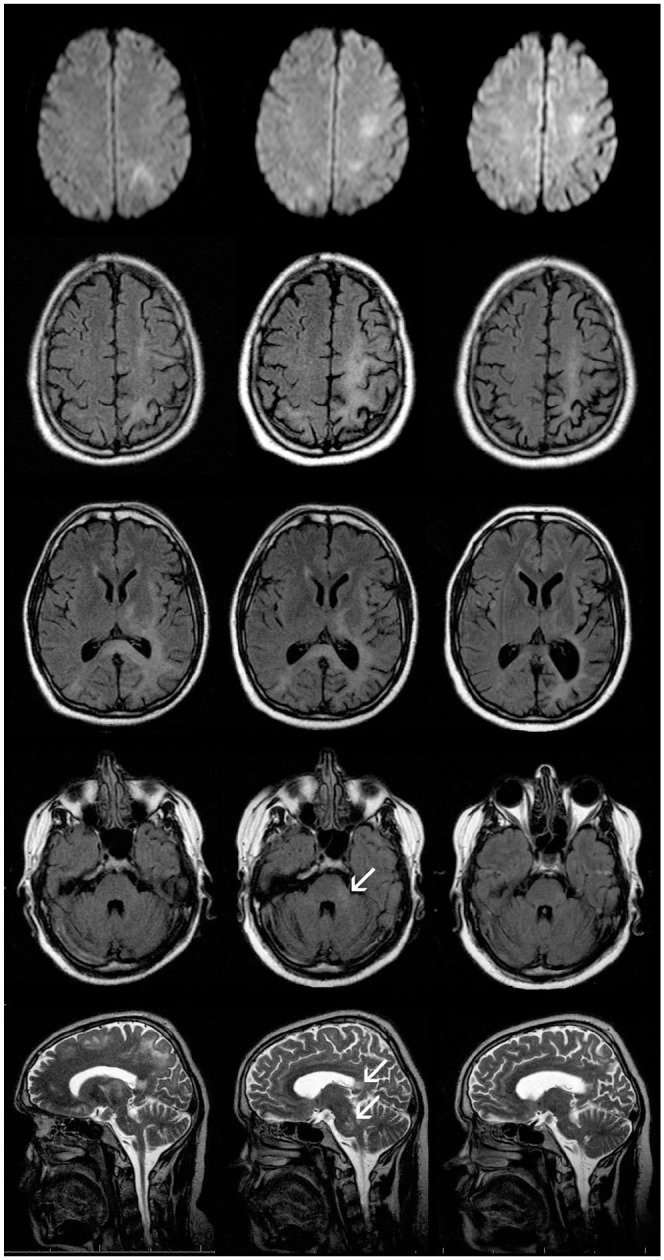
Axial DWI (upper row), T2-FLAIR (three middle rows) and sagittal T2-TSE (lower row) in patient 1. Left column shows images performed approximately 3 months after onset of the neurological symptoms (right sided homonymous hemianopsia and ataxia) and showing T2-hyperintense confluent subcortical lesions with left parieto-occipital focus but also involving left motoric and premotoric cortex, left parietal and occipital cortex, and subcortical white matter, posterior internal capsule, external capsule, and splenium of corpus callosum. In these areas, patchy diffusion restriction but no gadolinium enhancement is observed. The follow-up after 2.5 months (middle column) indicates progression of the subcortical PML lesions with left hemispheric accentuation (e.g. left cella media) but also new lesions in left pons and cerebellar pedunculus. Arrows indicate lesions in cerebellar pedunculus, splenium of corpus callosum, and pons. Approximately 6 months later (right column), decrease of the PML lesions with increasing atrophy and consecutive e vacuo enlargement of the inner CSF spaces can be noticed. Moreover, the infratentorial PML lesions are barely visible.
CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; DWI, diffusion weighted imaging; PML, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
