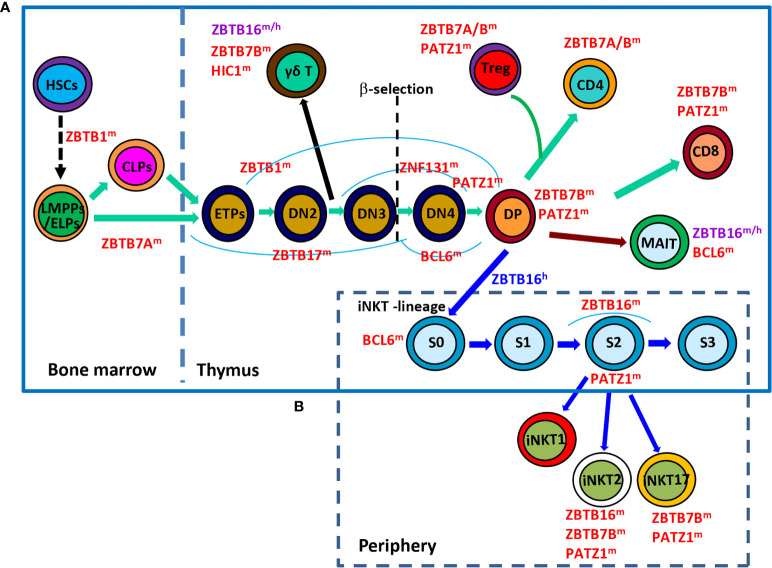
Figure 1.
Roles of ZBTB proteins in early T-cell development. (A), a schematic view of the stages most affected by ZBTB proteins along the early T-cell development program. ZBTB7A prevents the pre-mature differentiation of developing HSCs into DP T cells in the BM, while ZBTB1, ZBTB17, ZNF131, BCL6 and PATZ1 regulate the early development of conventional αβ+ T cells before the DP stage. Moreover, ZBTB16, ZBTB7B and HIC1 are important for the development/function of γδ+ T cells which diverge from the conventional T-lineage program at the DN2 stage. Since the DP stage, PATZ1, ZBTB7B & ZBTB7A modulate the differentiation of conventional CD4/CD8 SP cells and Treg cells, whereas ZBTB16 and BCL6 promote the development of unconventional MAIT cell and iNKT cells from DP cells. (B), a simplified overview of the development of iNKT cells in thymus as well as their functional maturation in the periphery. BCL6 promotes the transition of stage 0 (S0) iNKT cells into stage 1 (S1), after which ZBTB16 promotes their intrathymic expansion and effector differentiation. Moreover, PATZ1 and ZBTB7B fine-tune the subset differentiation of iNKT cells. ZBTB16 regulates iNKT cell development in humans as well. ZBTB proteins with the superscript ‘m’, ‘h’ or ‘m/h’ in the upper right corner indicate that these proteins are ascribed to mice, humans or both, respectively. S, stage.