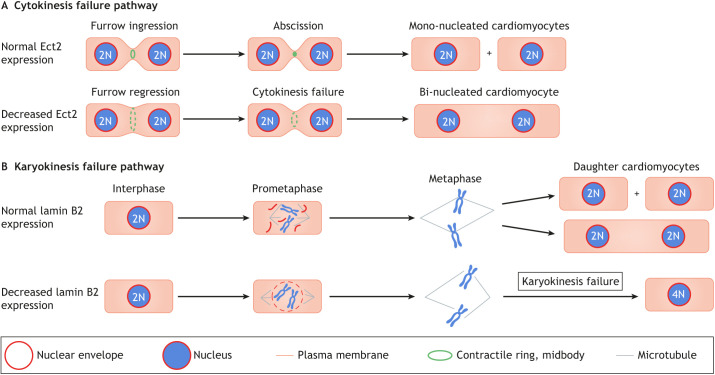
Fig. 2.
Cytokinesis and karyokinesis failure mechanisms in cardiomyocytes. (A) Ect2 has a function in mediating cleavage furrow ingression and abscission during cytokinesis. Normal expression of Ect2 during development thus allows for cytokinesis to occur (top). However, a reduction in Ect2 expression (bottom) causes cytokinesis failure, leading to the formation of bi-nucleated (or multi-nucleated) cardiomyocytes. (B) Lamin B2 has a function in karyokinesis, controlling nuclear envelope breakdown (NEB) during prometaphase. If lamin B2 levels are normal, karyokinesis can take place (top). However, insufficient lamin B2 levels (bottom) lead to incomplete NEB. This prevents complete spindle microtubule attachment to centromeres, resulting in prometaphase arrest and formation of polyploid daughter nuclei.