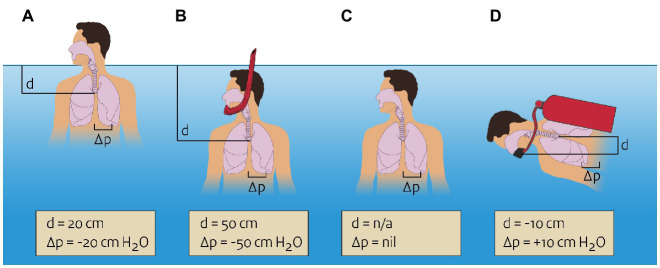
Figure 1.
Pressures in and around the lung during various types of immersion or submersion. Negative pressure differential means the pressure in the lung is lower than the pressure in the surrounding tissue. (A) Head-out-water-immersion, pressure differential of −20 cm H2O. (B) snorkeling, pressure differential of −50 cm H2O. (C) Swimming under water (breath holding), no pressure differential. (D) Diving with mouthpiece 10 cm below the lung, pressure differential of +10 cm H2O.