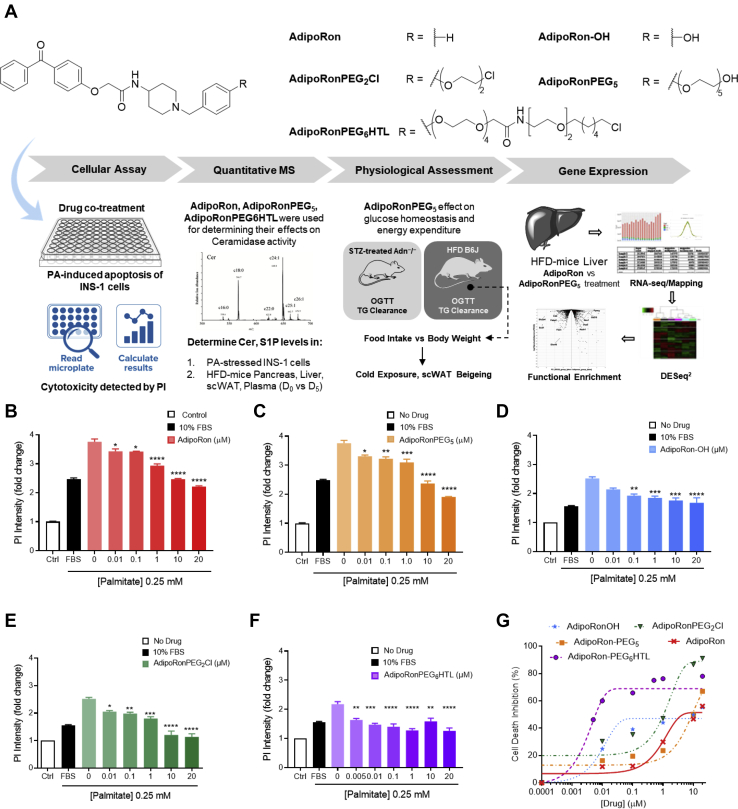
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of this work from compound screening to the mechanistic study. A: Experimental scheme of the present study including the structures of AdipoRon Analogs screened using PA-stressed INS-1 cells and quantified after treatment with PI using a platereader. AdipoRon analogs, namely AdipoRon for reference, AdipoRonPEG5 and AdipoRonPEG6HTL were selected to assess their effect on ceramide levels (Cer) in INS-1 cells and in mouse under HFD conditions (pancreas, liver, scWAT; plasma). This is followed by systematic testing of glucose, lipid and energy expenditure in HFD mouse treated with AdipoRonPEG5. A similar treatment on T1D mouse model (STZ-stressed Adn−/−) assessed the drug effect on insulin sensitivity and lipolysis. Finally, RNA-seq analysis of HFD-mouse liver was implemented to unravel the mechanisms by which AdipoRonPEG5 exerts its metabolic effects in the liver. B–F: AdipoRon analogs protect β-cells from palmitate-induced cell death. INS-1 β-cells were treated with different dosages of AdipoRon (B), AdipoRonPEG5 (C), AdipoRonOH (D), AdipoRonPEG2Cl (E), or AdipoRonPEG6HTL (F) for 24 h in the presence of palmitate (0.25 mM). The cells were then labeled with PI (1 mg/ml) for 5 min and measured on a fluorescence plate reader. PI fluorescence intensity was normalized against control cells that were not stressed with palmitate. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4). ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 versus 0 mM of compound. G: Dose-response curves of AdipoRon and derivatives in protecting INS1 cells from palmitate induced cell death.