FIGURE 3.
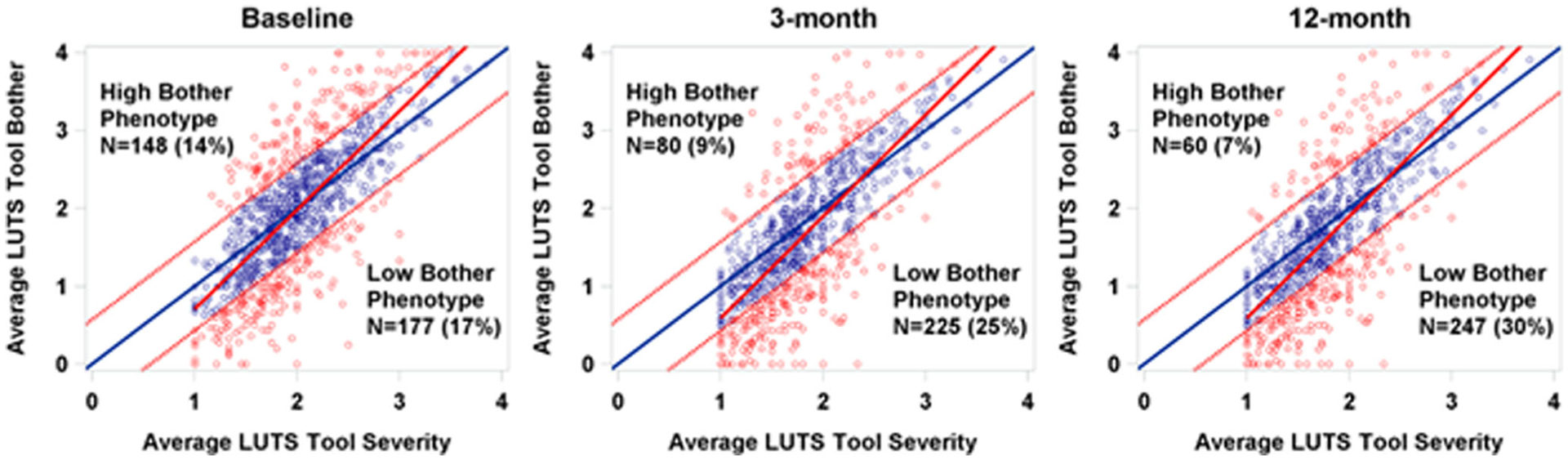
High bother phenotype distribution by timepoint. Average LUTS tool severity versus average LUTS Tool bother at baseline, 3 months, and 12 months.Scatterplot of average LUTS Tool bother by average LUTS tool severity, paneled by timepoint. Average bother (and severity) were calculated as the sum of bother (severity) responses divided by the number of symptoms endorsed (ie, severity response of at least 1). Average discordance was calculated as average bother minus average severity, and patients with average discordance 1 standard deviation above (or below) zero were considered to be in the high (low) bother phenotype. Solid blue lines represents equal average bother and severity (ie, average discordance of zero), solid red lines represent simple linear regressions (SLR) of bother regressed on severity, dotted red lines represent cutoffs for high and low bother phenotypes, blue circles represent patients in the “concordant bother” phenotype, and red circles represent patients in either the high or low bother phenotypes. LUTS, lower urinary tract symptoms
