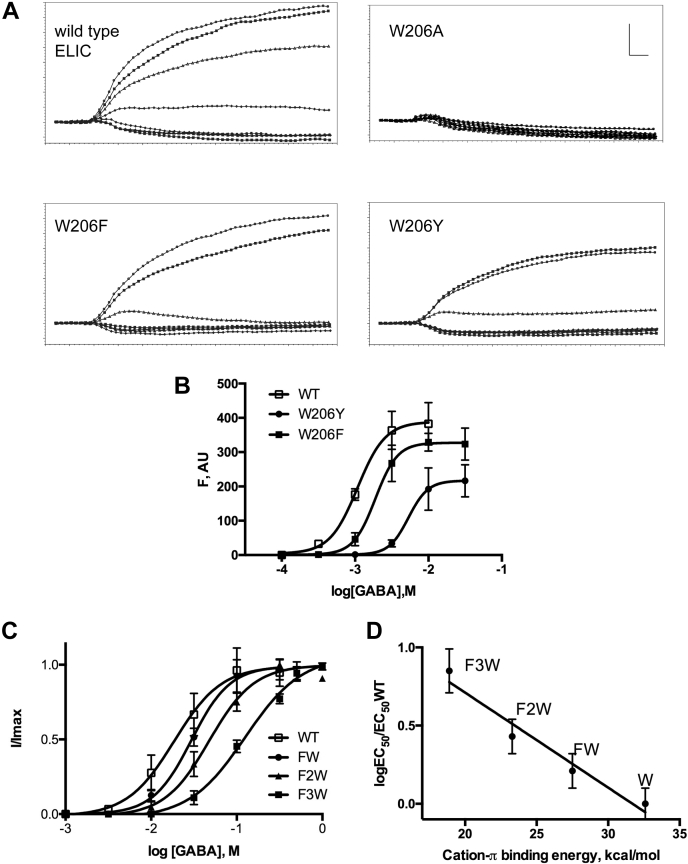
Figure 2.
Functional characterization of W206 in ELIC through natural and noncanonical amino acid mutagenesis.A, typical FlexStation responses to application of GABA (0, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, and 30 mM) at 20 s to HEK293 cells transfected with wild-type and mutant ELIC. Scale bar = 100 F, AU (arbitrary units) and 10 s. B, concentration–response curves from FlexStation data (mean ± SD, n = 4). EC50-values of these receptors were increased compared with wild-type (p = 0.0008), and for W206Y-containing receptors, maximal responses were smaller (p = 0.0013). Wild-type and mutant responses were compared using an ANOVA test followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. C, concentration–response curves for ELIC assayed in oocytes showing the effects of incorporation of the noncanonical amino acids FW, F2W, and F3W at position 206 (mean ± SD, n = 4). D, fluorination plot of W206 in ELIC. EC50-values for ELIC activation by the agonist GABA in wild type (WT) and 1-F, 2-F, and 3-F substituted W206 are indicated as FW, F2W, and F3W, respectively. The plot of the EC50-values relative to the cation-π binding energy reveals a linear correlation (r2 = 0.98), which is indicative of a strong cation-π interaction with W206 in ELIC.