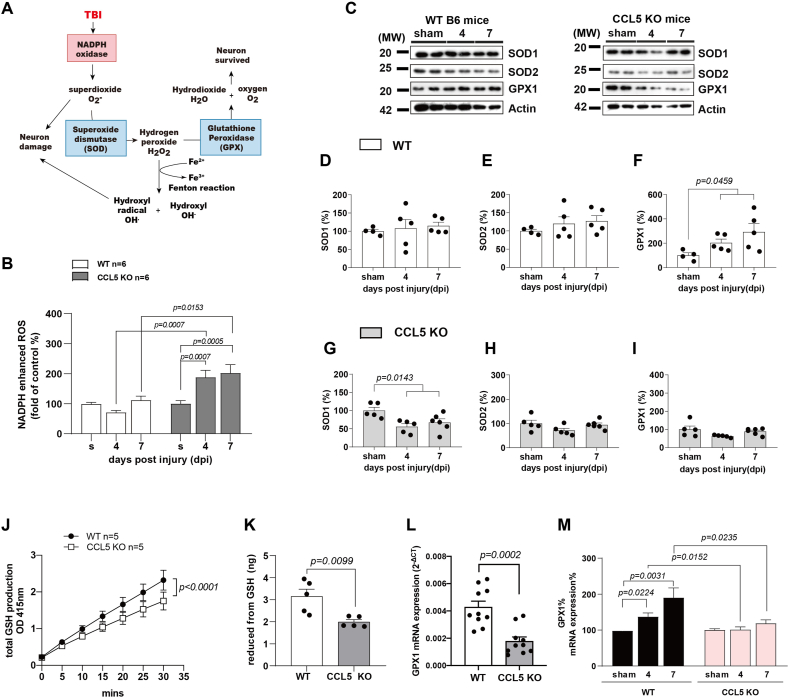
Fig. 4.
NADPH and antioxidant activation in WT and CCL5-KO mouse hippocampus after mild TBI. (A) Reactive oxygen species generation induced by brain trauma and related antioxidants in the scavenger pathway. (B) NADPH oxidase activity in mouse hippocampus tissue was measured at 4 and 7 dpi compared to sham group in WT and CCL5-KO mice. (Data was analyzed by t-test and presented as mean ± S.E.M.); (n = 6 in each group). (C–I) The protein levels of antioxidants - SOD1, SOD2 and GPX1 in mouse hippocampus at 4 dpi and 7 dpi and sham groups were analyzed. (C) The representative images of SOD1, SOD2 and GPX1 protein blots in WT mice and CCL5-KO mice. Quantitative results of SOD1 (D, G), SOD2 (E, H) and GPX1 (F, I) in WT mice and CCL5-KO mice. (Data was analyzed by One-way ANOVA and presented as mean ± S.E.M.) (n = 5 in each group). (J–K) The total GSH production and reduced form of GSH were measured and were lower in CCL5-KO mice compared to WT mice. (Data was analyzed by two-way ANOVA in A and t-test in B. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M.) Quantitative PCR analysis of GPX1 gene expression in WT and CCL5-KO mice control hippocampus (L) and mice with mTBI at 4 dpi and 7 dpi as well as in sham mice (M). (Data was analyzed by t-test and presented as mean ± S.E.M.)