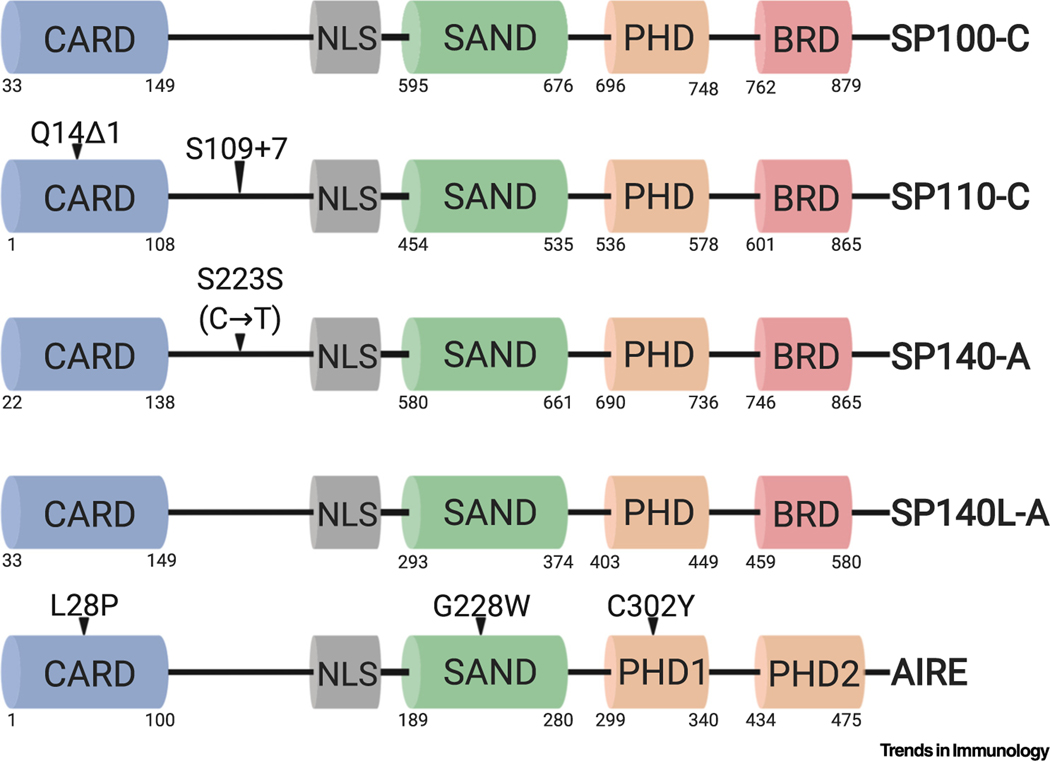
Figure 1. Functional Domains and Disease-Associated Mutations in Human Speckled Proteins (SPs) and Autoimmune Regulator (Aire).
SPs and Aire express highly similar caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), Sp100, Aire, NucP41/75, DEAF-1 shared domains (SANDs), and plant homeodomains (PHDs). The SP family PHD is similar to Aire’s PHD1. Aire contains two unique PHDs and lacks a bromodomain (BRD). Highlighted are representative mutations associated with immunological diseases. Depicted are full-length SP isoforms: SP100 isoform C (SP100-C), SP110 isoform C (SP110-C), SP140 isoform A (SP140-A), and SP140-like (SP140L) isoform A (SP140L-A). Protein domains are depicted with corresponding amino acid residue positions underneath. The synonymous mutation depicted in SP140 is a cytidine-to-thymidine nucleotide mutation. Δ1, one-nucleotide deletion; +7, seven-nucleotide insertion. This figure was created using BioRender (https://biorender.com/).