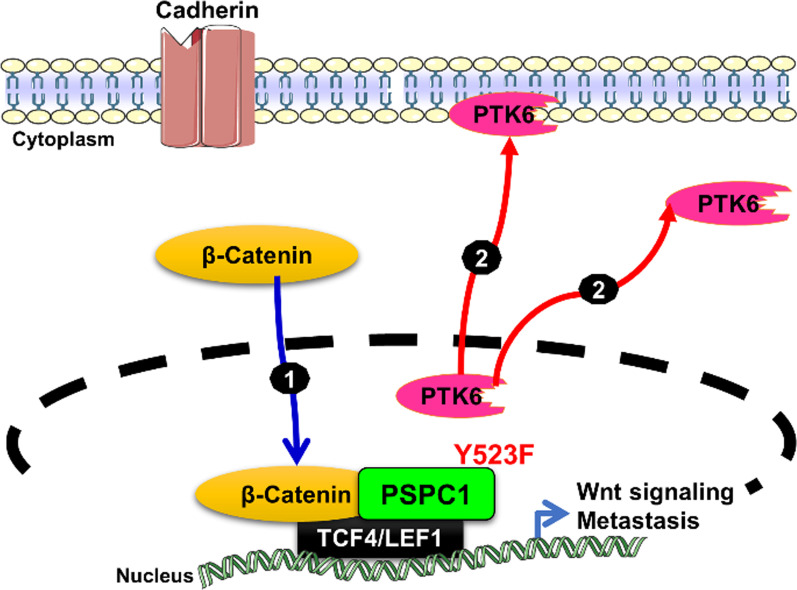
Fig. 2.
PSPC1 is the contextual determinant of PTK6/β-catenin reciprocal nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. (1) In cells of advanced cancer with high PSPC1 expression, PSPC1 upregulation or mutation of amino acid residue 523 in PSPC1 from tyrosine to phenylalanine (PSPC1-Y523F) can determine oncogenic subcellular translocation to exert synergistic effects on the translocation of cytoplasmic β–catenin to the nucleus and preferentially interact with PSPC1 to facilitate synergistic oncogenic effects (2) PTK6 can translocate to the cytoplasm and cell membrane as an oncogene to facilitate synergistic oncogenic effects such as epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), Wnt3a autocrine signaling and stemness promoting metastasis