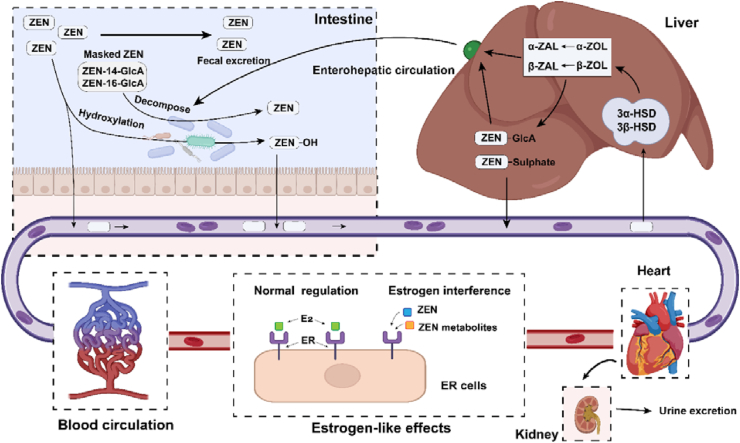
Fig. 2.
The metabolic process of zearalenone (ZEN) in animals. Intestine: After intestinal absorption of ZEN, some part of ZEN is affected by intestinal microbes and is hydroxylated, and the remaining ZEN is excreted with feces. Liver: Some ZEN metabolism and detoxification products are excreted into the intestines through bile, entering the enterohepatic circulation. The metabolism and detoxification products are absorbed into the blood circulation, and part is excreted in urine and milk. ER cells: ZEN and its metabolites compete for the binding site of E2 and interfere with the normal function of estrogen. ZAL = zearalanol; ZOL = zearalenol; HSD = hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; GlcA = glucuronic acid; E2 = 17-β estradiol; ER = estrogen receptor.