Figure 2.
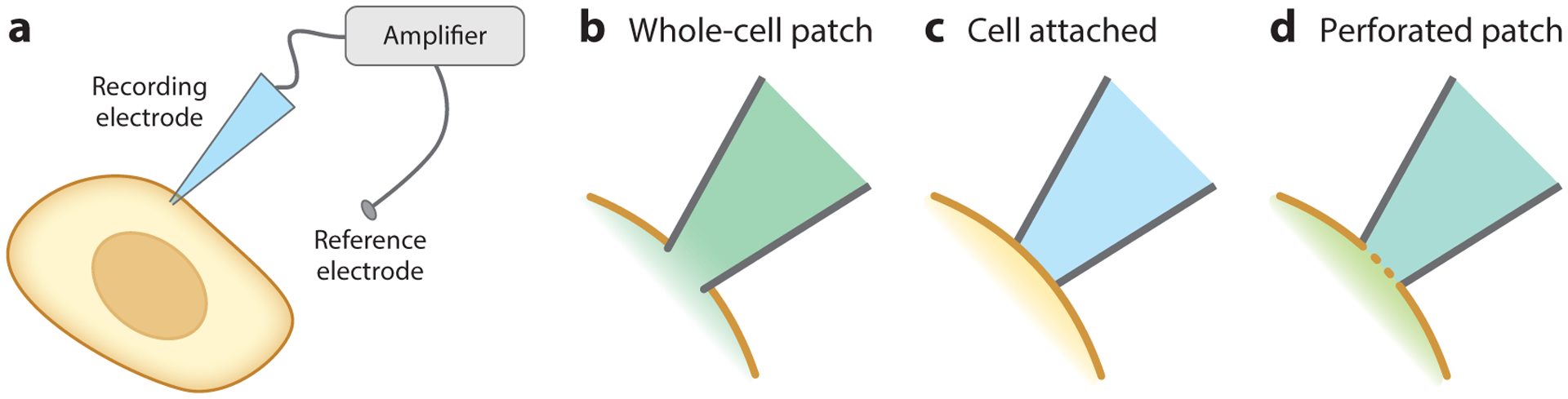
Electrophysiological configurations for Vmem recording. (a) General schematic for electrode-based Vmem recordings, in which a cell comes into direct contact with an electrode. Voltage is measured as the difference between the recording electrode and a reference electrode in the bath solution. (b–d) Close-up of the interface between the membrane and the electrode in different electrophysiology configurations. (b) In whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology, the plasma membrane is ruptured, and the cytosol mixes with the recording electrode solution. (c) In the cell-attached configuration, the plasma membrane is left intact. (d) In perforated patch, the membrane is not ruptured, but ionophores introduced into the recording solution allow ionic exchange across the membrane.
