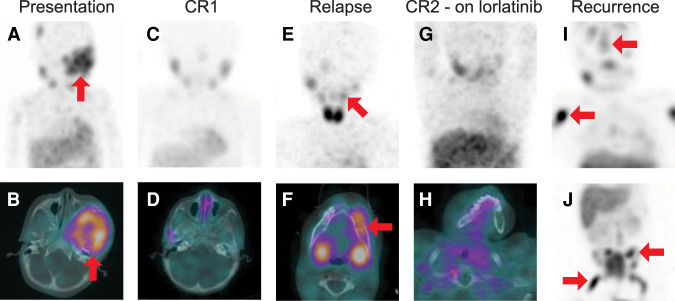
Figure 1.
Serial 131I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/computed tomography (CT) studies. (A) Baseline maximum intensity projection (MIP) image of the head, neck, and chest and (B) SPECT/CT image through the skull base demonstrate bone metastatic disease including a large, radiotracer-avid skull base lesion (red arrows). (C) MIP and (D) axial SPECT/CT through the skull base following initial therapy show complete resolution of the radiotracer-avid metastatic disease. (E) MIP and (F) axial SPECT/CT through the mandible at the time of recurrence demonstrate multifocal radiotracer-avid bone metastases, including a lesion in the left mandibular body (red arrows). The MIP is obliqued in order to project the mandibular lesion away from physiologic uptake in the salivary glands. (G) MIP and (H) axial SPECT/CT through the mandible after therapy shows complete resolution of radiotracer-avid disease. (I,J) MIP images of the head, neck and chest (I) and of the abdomen and pelvis (J) demonstrate extensive new bone metastases. Representative lesions in the calvarium, right humerus, left iliac, and right femur are demarcated with red arrows.