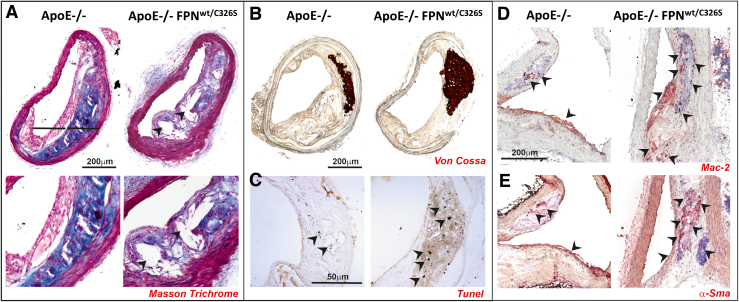
FIG. 4.
NTBI triggers intraplaque lipid accumulation, cell apoptosis, macrophage recruitment, VSMC phenotypic switch, and vascular calcification. (A, B) Representative images of common carotid artery of ApoE-null and ApoE-null FPNC326S mice stained with (A) Masson's trichrome, (B) Von Cossa, and (C) Tunel stains. (D, E) Representative images of innominate arteries of ApoE-null and ApoE-null FPNC326S mice stained with antibodies against (D) Mac-2 and (E) α-Sma. (A) The Masson trichrome stain shows reduced collagen deposition (blue) and increased lipid droplets (white) within the atherosclerotic plaque of ApoE-null FPNC326S compared with ApoE-null control mice. Arrowheads show lipid-filled areas. (B) The Von Cossa stain shows the presence of dark brown-stained intraplaque calcifications, which are bigger and more frequent in ApoE-null FPNC326S mice. (C) The Tunel stain reveals the presence of multiple Tunel-positive dark apoptotic cells within the plaque of the ApoE-null FPNC326S mice, which are almost absent in the ApoE-null mice. Arrowheads show Tunel-positive cells. (D) Mac-2 stains show a higher number of Mac-2-positive macrophages in the plaque of ApoE-null FPNC326S mice compared with ApoE-null mice. Arrowheads point at Mac-2-positive cells. (E) α-Sma stains show α-Sma-positive cells in the plaque of ApoE-null and ApoE-null FPNC326S mice. Arrowheads point at α-Sma-positive cells. The partial overlapping of Mac-2 and α-Sma stain suggests that VSMCs might undergo a phenotypic switching toward macrophage-like cells. αSMA, α smooth muscle actin; Mac2, macrophage 2 protein or Galectin 3. Color images are available online.