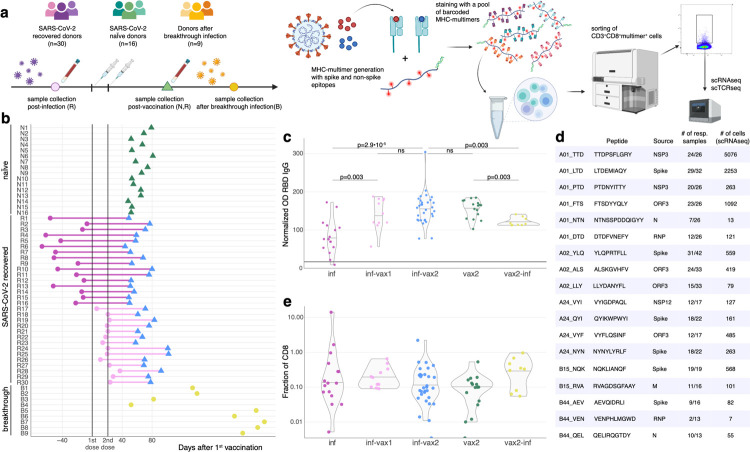
Figure 1. Measuring CD8+ T cell epitope-specific responses after diverse SARS-CoV-2 exposures.
a. Study design. Selected spike and non-spike SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes were loaded on recombinant biotinylated MHC-monomers. Resulting peptide-MHC complexes were polymerized using fluorescently labeled and DNA-barcoded dextran backbones. Next, we stained PBMC samples with pools of MHC-multimers, isolated bound cells using FACS, and performed scRNAseq, scTCRseq, and CITEseq using the 10X Genomics platform. b. Time of blood sampling for each donor is shown relative to the first dose of mRNA vaccine. c. Anti-RBD IgG antibody levels in previously infected individuals increase after BNT162b2 vaccination. Anti-RBD IgG levels in the plasma were determined by ELISA. The normalized OD is the percent ratio of the sample OD to the OD of the positive control for each plate. Plasma was collected from previously infected donors prior (purple, inf), after 1 vaccine dose (inf-vax1, pink), and after 2 vaccine doses (inf-vax2, blue); SARS-CoV-2 naive donors after the full vaccination (vax2, green), and donors that were infected after vaccination (breakthrough, vax2-inf, yellow). All comparisons were done with Mann-Whitney U test, p-values are reported after Benjamini-Hochberg correction. Central line on violin plots depicts the median. d. List of SARS-CoV-2 epitopes used in this study and summary statistics for resulting epitope-specific response. e. Total frequency of MHC-dextramer-positive cells is similar in all studied groups (p>0.05 for all pairwise comparisons, Mann-Whitney U test after multiple test correction). Percentage of MHC-multimer-positive cells from all CD8+ T cells measured by flow cytometry is shown on a log10-scale. Central line on violin plots shows the median.