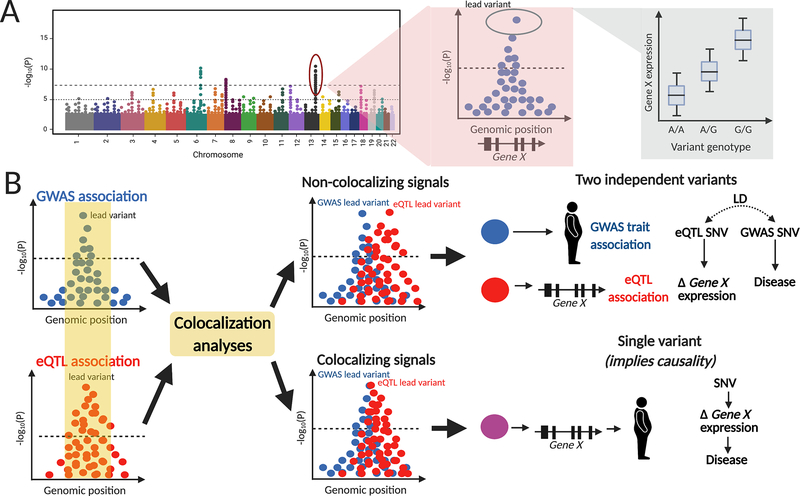
Figure 4. Colocalization of genetic signals offers evidence of causality.
(A) Example of an eQTL study, where the outcome is gene expression and variant genotypes are tested across the genome to find specific loci that are associated with differential gene expression (eQTL levels). (B) Colocalization analysis of GWAS and eQTL studies, with colocalization of signals offering mechanistic evidence for a potential causal variant. In the case of non-colocalization, the two variants are in linkage disequilibrium (LD) meaning they are often inherited together as a haplotype. Abbreviations: eQTL – expression quantitative trait loci, GWAS – genome-wide association study, LD – linkage disequilibrium.