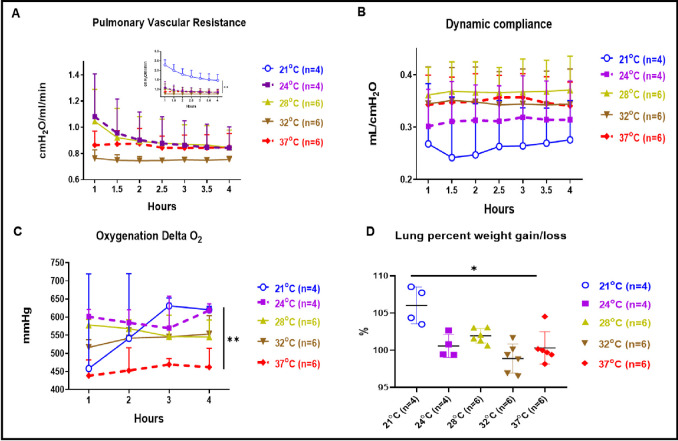
Fig 1. Physiological variables and oxygenation parameters.
(A) PVR at 21°C was significantly higher than those at 37°C (p<0.01) (see Fig 1A insert). PVR at 32°C were with a lower but not statistically different value compared to PVR at 37°C. PVR at 28°C and 24°C were comparable to PVR at 37°C. (B) Cdyn at 21°C and 24°C showed a not significantly different lower value than those at 37°C. Cdyn at 28°C and 32°C were similar to Cdyn at 37°C. (C) Perfusate oxygenation (delta PO2 or left atrial pressure of oxygen minus pulmonary arterial pressure of oxygen) was significantly improved at 24°C and 21°C (p<0.01) and were higher at 28°C and 32°C although this difference was not statistically different from the control EVLP performed at 37°C. (D) Percentage of gain/loss in lung weight after 4 hours of EVLP was significantly higher at 21°C when compared to 37°C normothermic temperature (p<0.05).