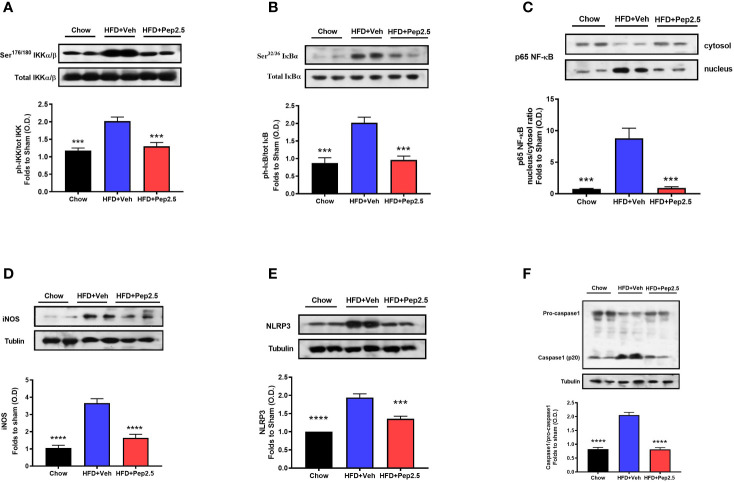
Figure 6.
Peptide 19-2.5 reduces liver inflammation via the inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway and the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in the liver of HFD-fed mice. Liver samples were collected at the end of the experiment and the NF-κB signaling pathway, as well as the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome were assessed. Densitometry analysis of the bands is expressed as relative optical density (O.D.) of the (A) phosphorylation of IKKα/β at Ser178/180 corrected for the corresponding total IKKα/β content and normalized using the related chow band; (B) phosphorylation of IĸBα at Ser32/36 corrected for the corresponding total IĸBα content and normalized using the related chow band; (C) NF-κB p65 subunit levels in both, cytosolic and nuclear fractions expressed as a nucleus/cytosol ratio normalized using the related chow bands; (D) inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression corrected for the corresponding tubulin band. (E) NLRP3 activation, corrected against tubulin and normalized using the related chow bands and the (F) proteolytic cleavage of pro-caspase-1 to activated caspase-1 and normalized using the related chow band. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; chow (n = 5), HFD+Veh (n = 6), HFD+Pep2.5 (n = 6). ***P< 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 vs. HFD+Veh.