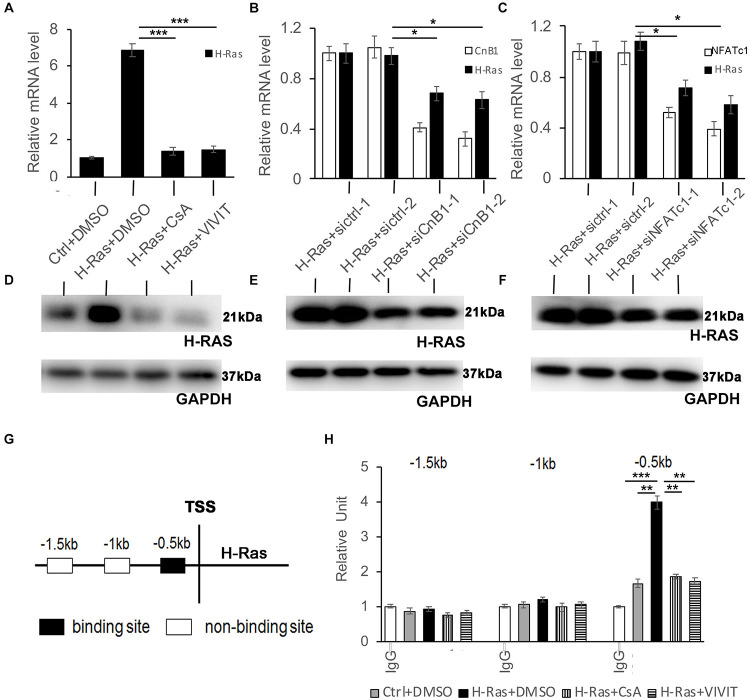
FIGURE 6.
NFATc1 regulates H-Ras expression in human keratinocytes overexpressing H-RasA. Human keratinocytes were infected with a H-RasG12V expressing or a control retrovirus and were then treated with the calcineurin/NFAT inhibitors CsA, VIVIT, or DSMO as a negative control for 24 h, then were collected for quantitative RT-PCR analysis of H-Ras expression. (B-C) Human keratinocytes were transfected with two independent siRNAs of CnB1 (siCnB1-1 and siCnB1-2) in panel (B) or NFATc1 (siNFATc1-1 and siNFATc1-2) in panel (C) or scramble siRNAs (siCtrl) in both panels (A,B) as a control 2 days after transfection, the cells were infected with a H-RasG12V expressing or a control retrovirus, and 24 h later, the treated cells were collected for quantitative RT-PCR analysis of CnB1 (B) or NFATc1 (C), and H-Ras expression. (D–F) Western-blot analysis of H-Ras protein levels in cells from panels (A–C), respectively. GAPDH as loading control. (G,H) Three potential binding sites located upstream of the H-Ras transcriptional start site (TSS) as indicated in panel (G) were analyzed by CHIP assays, and CHIP products derived from human keratinocytes with different conditions as labeled were analyzed by RT-PCR in panel (H). All experiments were carried out three times, and error bars represent means ± SD; p values are indicated with “*,” *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.005 when comparing two corresponding groups indicated with the black lines by Student’s t-test.