Fig. 5. Soluble phosphatases shape PKA-dependent phosphorylation in HT-29 cells.
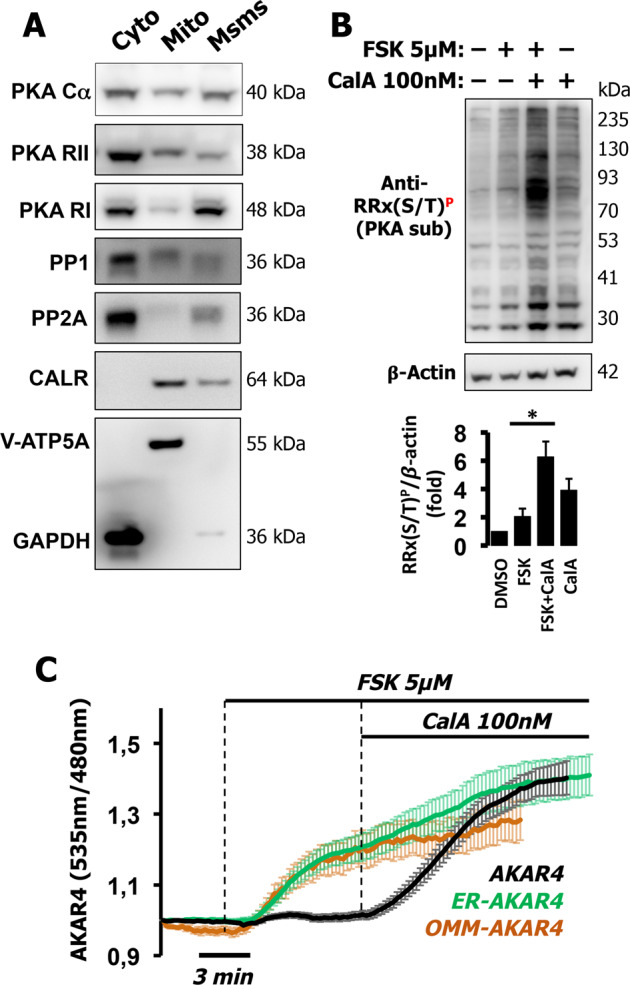
A Western blotting of PKA components and phosphatases in cytosolic/soluble (cyto), mitochondria-enriched (Mito), and microsomal-enriched (Msms) fractions from HT-29 cells. An antibody mixture against ATP synthase subunit alpha (V-ATP5A) and GAPDH assessed mitochondrial enrichment and cytosol, respectively, while calreticulin (CALR) was used to determine ER enrichment. B Total cell lysates (40 µg) of HT-29 were treated with FSK (5 µM), Calyculin A 100 nM (CalA), or both combined and the phosphorylation status of endogenous PKA substrates was assessed by the phospho-PKA substrate-specific antibody, RRX(S/T)P. Combination of CalA and FSK produced a dramatically greater responses than those of the individual drugs alone, indicating an additive effect as summarized in the quantification histogram (inset). β-actin was used as loading control. Experiments were repeated at least three times. C HT-29 cells expressing AKAR4 (black), OMM-AKAR4 (orange), or ER-AKAR4 (green) challenged with FSK (5 µM) followed by CalA (100 nM) to block phosphatases. Averaged traces ± SD of 12 cells for AKAR4, 15 cells for OMM-AKAR4, and 12 cells for ER-AKAR4, from three independent experiments for each sensor.
