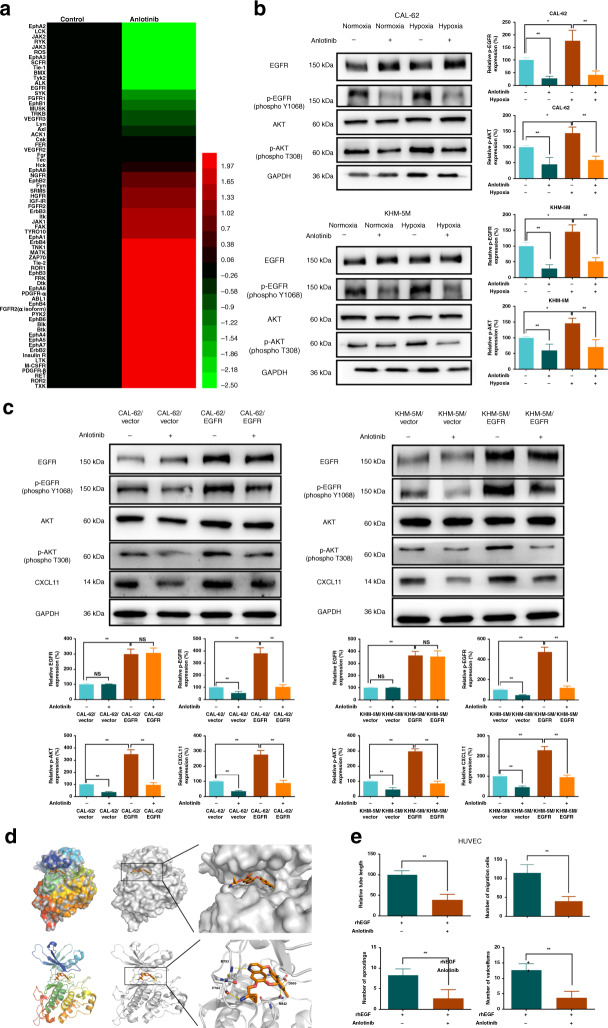
Fig. 5. Anlotinib directly targets EGFR kinase.
a Heatmap of the molecular changes from the phospho-RTK antibody array, which was completed by using the same samples like that in the angiogenesis antibody array. b Expression level of p-EGFR and p-AKT was examined when CAL-62 and KHM-5M cells were treated by anlotinib under normoxia and hypoxia. c CXCL11 production was increased in EGFR overexpression cells, and anlotinib could more efficiently inhibit the EGFR-AKT signalling and CXCL11 production in CAL-62/EGFR and KHM-5M/EGFR cells compared with their Vector controls. d Cartoon representations of the anlotinib’s binding pocket in EGFR in visualised models of molecular docking. Residues of Met793, Pro794, Asn842 and Asp855 of EGFR were predicted to interact with anlotinib by hydrogen bonds. The ligands are shown in orange sticks, while proteins are depicted in cartoon representation with key residues. Hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashed lines. e Anlotinib repressed angiogenetic abilities by directly inhibiting HUVEC, including tubule formation, migration, 3D buddings and CAM vessels. All data are obtained from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.