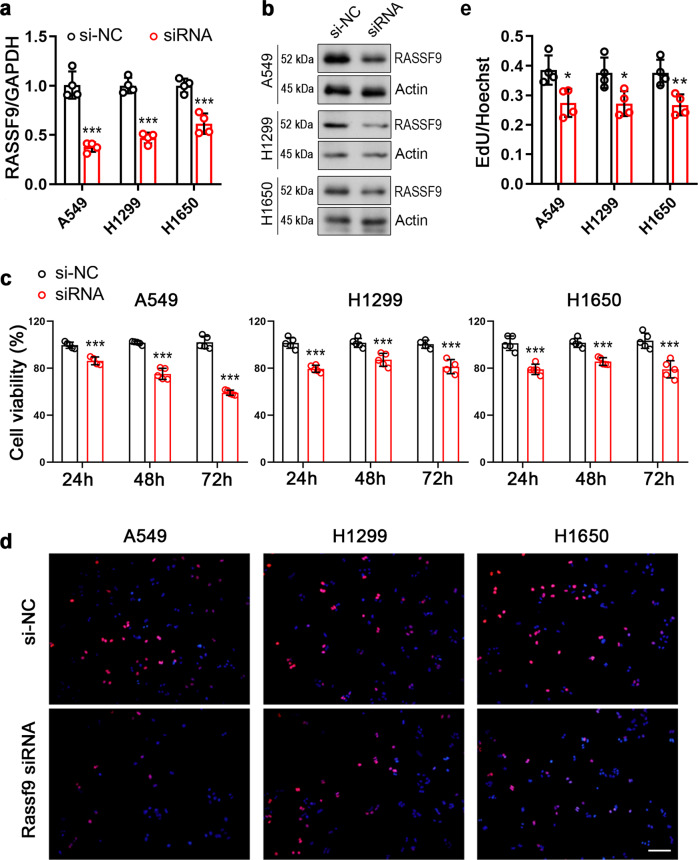
Fig. 3. Knockdown of Rassf9 suppresses NSCLC cell proliferation.
a Knockdown of Rassf9 by siRNA. A549, H1299, and H1650 cells were transfected with Rassf9 siRNA or negative control (si-NC). Forty-eight hours post-transfection, total RNA was extracted for gene expression analysis by qRT-PCR and GAPDH was used as a house-keeping gene. b The protein levels of RASSF9 were reduced by siRNA. Cell treatments were described in (a). Protein levels were analyzed by western blot and Actin was used a loading control. c Knockdown of Rassf9 decreases NSCLC cell viability. A549, H1299, and H1650 cells were transfected with Rassf9 siRNA or si-NC. Cell viability was analyzed by the method of MTT at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h post-transfection. d Knockdown of Rassf9 reduces EdU incorporation. A549, H1299, and H1650 cells were transfected with Rassf9 siRNA or negative control (si-NC). Forty-eight hours post-transfection, cell proliferation was analyzed by EdU immunofluorescence assay. Scale bar = 500 μm. e Quantitative analysis of EdU incorporation. Data are presented as means ± SD (error bars). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Student’s t-test.