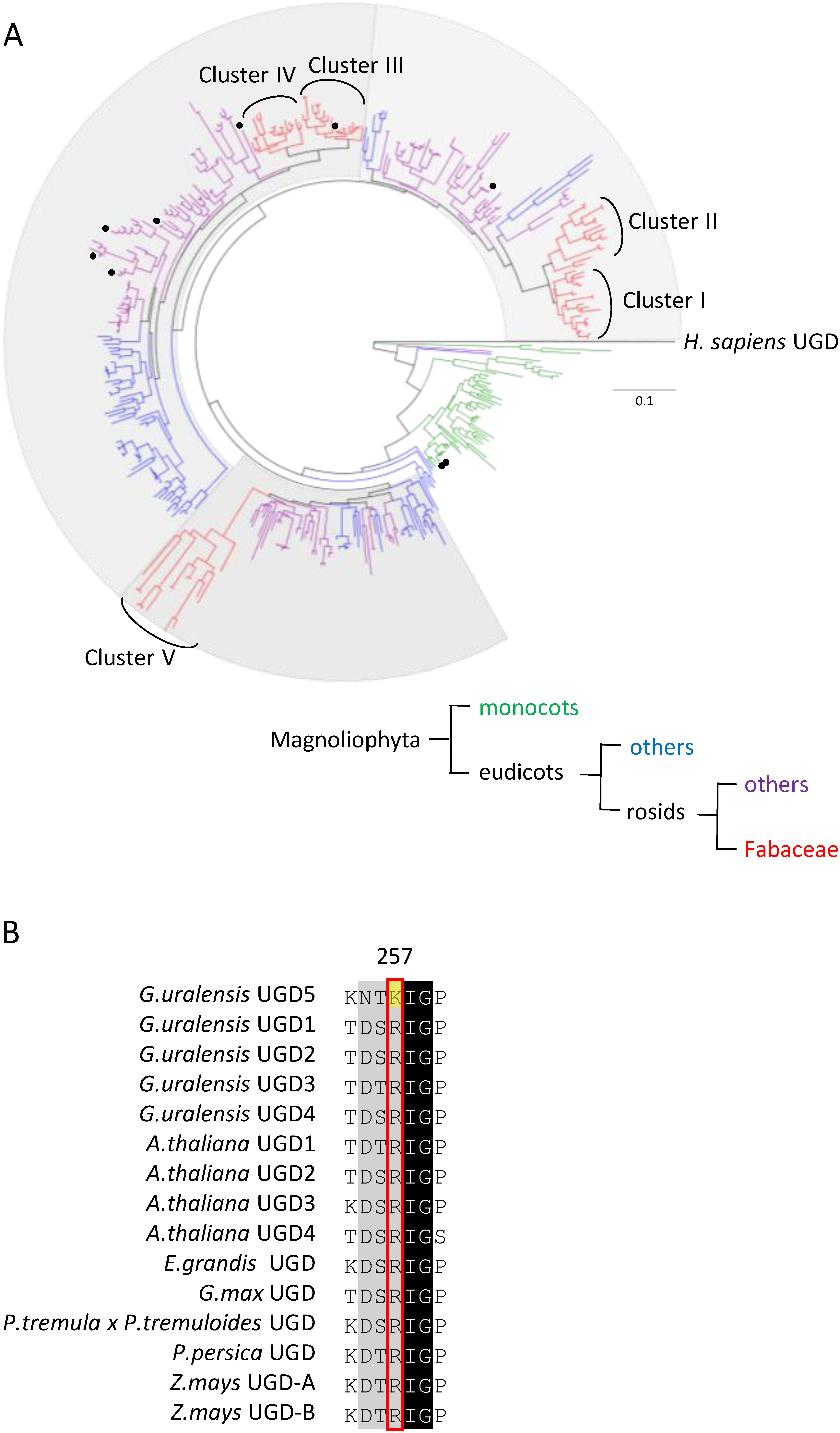
Figure 5. Phylogenetic tree and alignment of amino acid sequences of GuUGDs and characterized plant UGDs. (A) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of UGD homologous proteins from various plants, rooted on Homo sapiens UGD as the outgroup. The scale measures evolutionary distance in substitutions per amino acid. Protein sequences were retrieved from GenBank by blastp search with the GuUGD sequences as queries. Black circles on the tree indicate previously characterized UGDs. Monocots are shown in green. Eudicots except for rosids are shown in blue. Rosids except for Fabaceae are shown in purple. Fabaceae are shown in red. Fabaceae UGD homologous proteins are separated into five clusters. (B) Alignment of amino acid sequences of GuUGDs and characterized plant UGDs. We made the alignment using BioEdit with ClustalW. The amino acid residue shown with the yellow background is specific to GuUGD5.