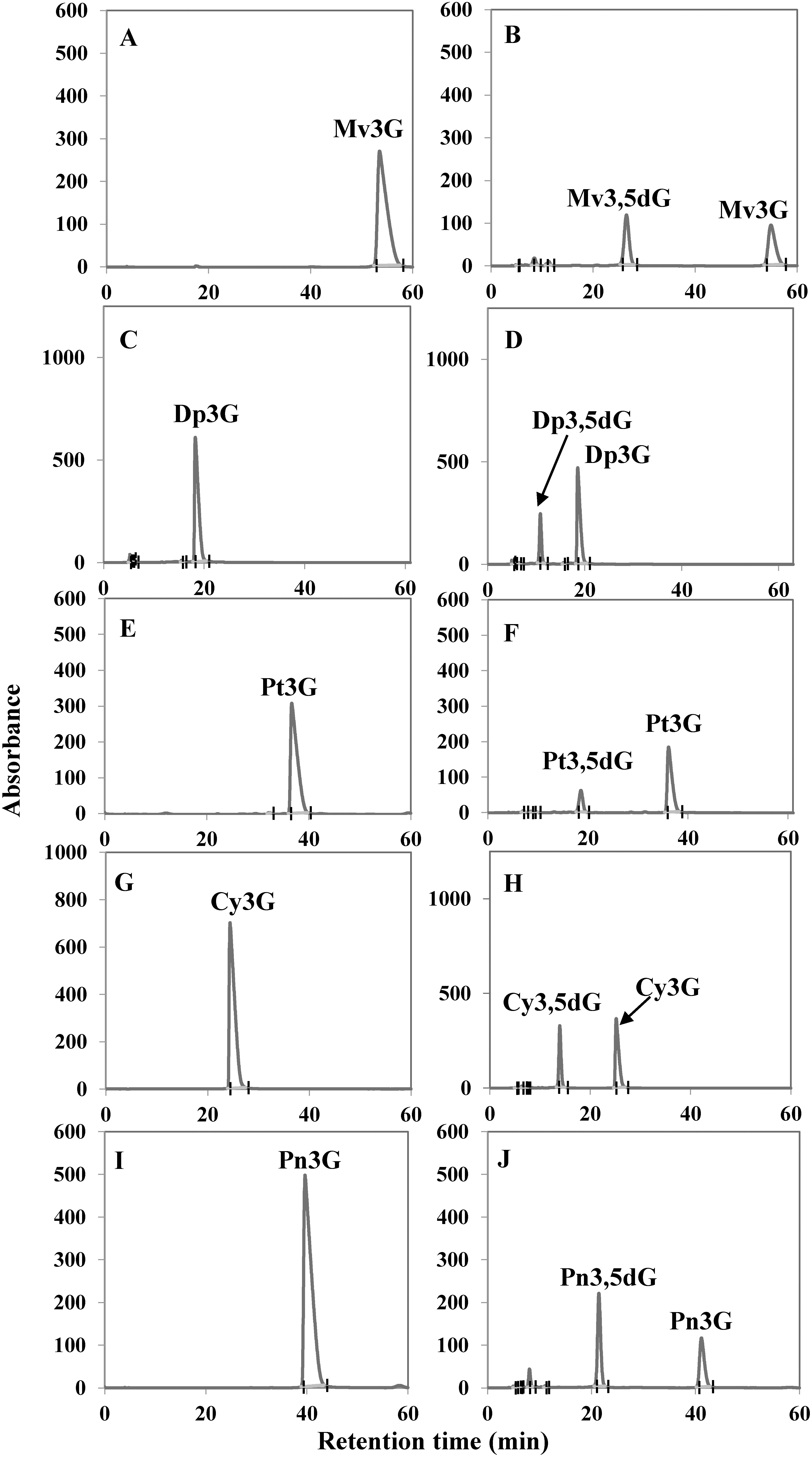
Figure 4. HPLC analysis of Cpur5GT reaction products obtained from the in vitro enzyme assay. (A–J) Five potential substrates including Mv3G (A, B), Dp3G (C, D), Pt3G (E, F), Cy3G (G, H), and Pn3G (I, J) were incubated without (A, C, E, G, I) or with (B, D, F, H, J) the purified Cpur5GT. UDP-glucose was used as the sugar donor.