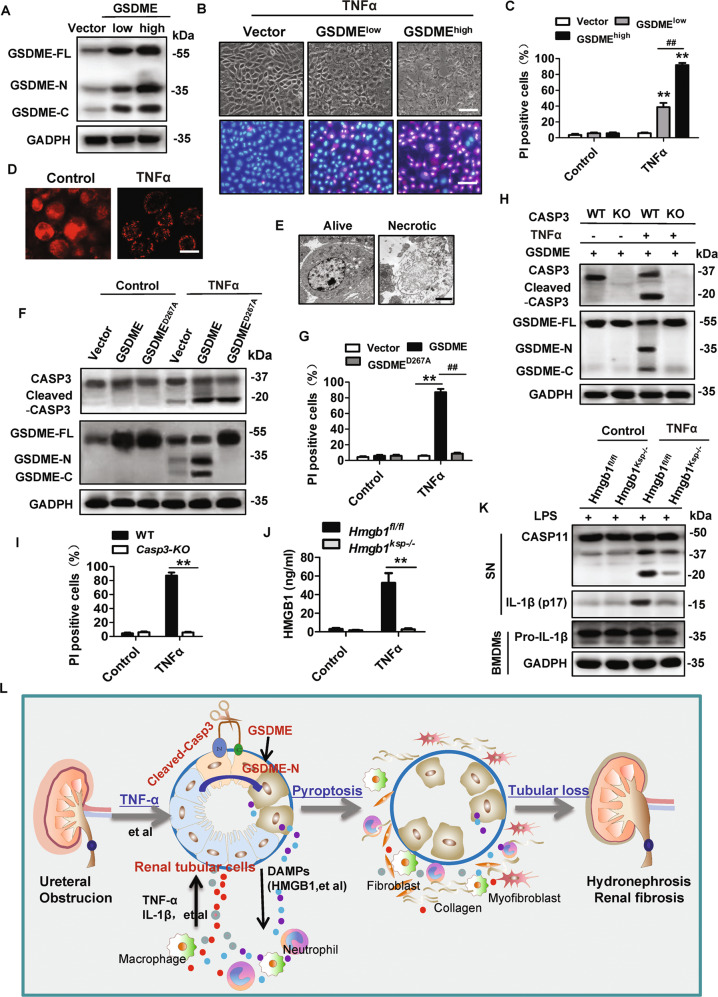
Fig. 8. Caspase3 cleaved GSDME in over-expressing GSDME of renal tubular cells (RTCs) in vitro to induce cell death and release HMGB1.
A–E RTCs from WT mice were infected with lentivirus encoding vector or GSDME for 44 h and then treated with or without 100 ng/ml TNFα for 24 h under the condition of oxygen-glucose-serum deprivation (OGSD). The control groups were treated with OGSD but without TNFα. Western blot analysis of GSDME expression in (A). PI (red) and Hoechst (blue) staining were used to assessed cell death cells in (B) (Scale bar = 100 μm). The percentage of PI-positive cells was counted as (C). n = 6. **P < 0.01 vs. Vector group; ##P < 0.01 vs. Low dose virus encoding GSDMD group. Cells were immunostained for GSDME and representative images obtained by confocal microscope were shown as (D) (Scale bar = 25 μm). Representative electron micrographs of live and necrotic RTCs are shown in (E) (Scale bar = 3 μm). F–G RTCs from WT mice were infected with lentivirus encoding nothing (vector) or GSDMEwt, or GSDMED267A for 44 h and then treated as (A). Western blot analyzed the cleavage of GSDME as (F). PI-positive cells were counted in (G). n = 6. **P < 0.01, ##P < 0.01. H–I RTCs from Casp3+/+ and Casp3−/− mice were infected with lentivirus encoding GSDME for 44 h and then treated as (A). Western blot analyzed the cleavage of caspase-3 and GSDME (H) and cell death was evaluated by counting PI-positive cells (I). n = 6. **P < 0.01, ##P < 0.01. J RTCs were isolated from Hmgb1fl/fl or Hmgb1Ksp−/− (Ksp-cre × Hmgb1fl/fl) mice, and then treated as (A). ELISA analyzed the level of HMGB1 in the extracellular supernatants. n = 6. **P < 0.01. K BMDMs from WT mice were pre-incubated with LPS (500 ng/ml) for 4 h and then were treated with culture supernatants for 24 h, which were collected from wild type or Hmgb1-deficient RTCs after treated as (A). Western blot analyzed the expression of caspase 11 and IL-1β. n = 4. L Schematic model: Caspase3/GSDME-mediated pyroptosis in the development of obstructive nephropathy.