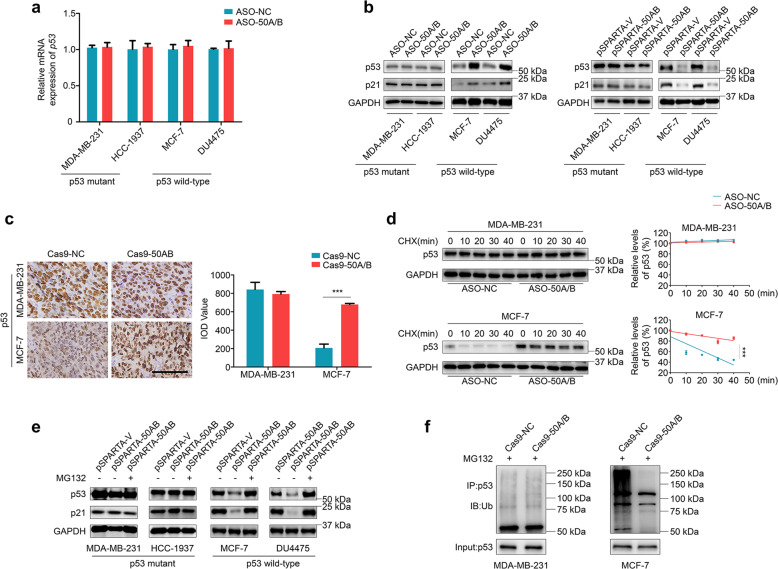
Fig. 3. SNORD50A/B induces ubiquitin-proteasome degradation of wild-type p53.
a The effect of SNORD50A/B knockdown on mRNA expression of p53 in the indicated cells was evaluated by qRT-PCR. 18S rRNA was used as a reference gene. b The effects of knockdown (left panel) and ectopic expression (right panel) of SNORD50A/B on protein expression of p53 and its downstream target p21 in the indicated cells were evaluated by western blot analysis. GAPDH was used as a loading control. c The p53 levels in in the indicated xenograft tumors were evaluated by IHC staining (left panels). Scale bars, 200 μm. The expression levels were calculated with IOD value from three different views (right panel). d MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells were treated with 200 µg/mL CHX for the indicated times. Western blot analysis was then performed to analyze protein expression of p53 (left panels). GAPDH was used as a loading control. The band intensity of p53 in the SNORD50A/B-knockdown cells was normalized to that of GAPDH, and then normalized to that in the control cells (right panels). e The indicated cells were treated with 25 μM proteasome inhibitor MG132 for 3 h, and western blot analysis was then performed to evaluate the expression of p53 and its target p21. GAPDH was used as a loading control. f MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells stably knocking out SNORD50A/B and control cells were treated with 25 μM MG132 for 2 h before harvesting. Lysates were then incubated with anti-p53 antibody and conjugated with agarose. Bounding proteins were analyzed by immunoblot with anti-ubiquitin (Ub) antibody to assess p53 ubiquitination. Data were presented as mean ± SD. ***, P < 0.001.