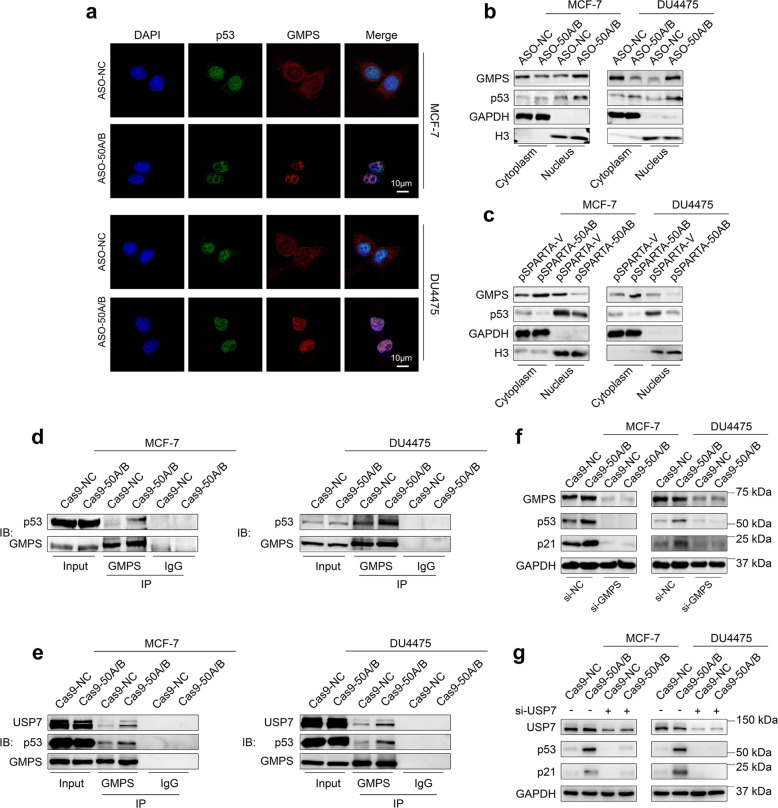
Fig. 4. SNORD50A/B reduces p53 stability by impairing nuclear translocation of GMPS.
a Immunofluorescence was performed to determine the translocation of GMPS and the co-localization of GMPS and p53 in MCF-7 and DU4475 cells knocking down SNORD50A/B. b, c Protein expression of GMPS and p53 in the cytoplasm and nucleus of the indicated cellsMCF-7 and DU4475 cells knocking down or ectopically expressing SNORD50A/B was evaluated by western blot analysis. GAPDH and total histone H3 were used as loading controls. d Cell lysates of MCF-7 and DU4475 cells knocking out SNORD50A/B were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to GMPS (mouse clonal) or IgG, and immunoblotted with antibody to p53 (rabbit clonal). e Immunoprecipitation was performed to verify the formation of GMPS-p53-USP7 complex in MCF-7 and DU4475 cells knocking out SNORD50A/B. MCF-7 and DU4475 cells knocking out SNORD50A/B and control cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting GMPS (f) or USP7 (g) for 48 h, western blot analysis was then performed to evaluate the expression of p53 and p21. GAPDH was used as a loading control.