FIGURE 2.
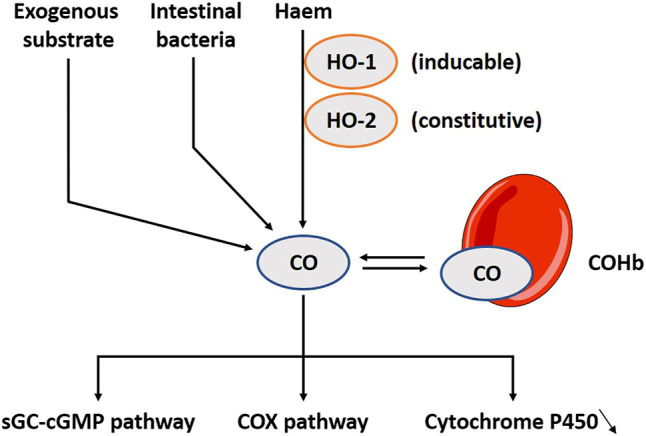
The carbon monoxide (CO) pathway including involved substrates, enzymes and downstream pathways. CO is produced during the catabolism of haem by two oxygenase proteins, HO-1 and HO-2, but it can also be released in small amounts by intestinal bacteria. Interestingly, several exogenous substrates to induce the pathway exist. CO prefers binding hemoglobin, and this complex has a long half-life time up to 4 h. CO’s biological functions are related to the activation of sGC; subsequently influencing cGMP, but other pathways such as the COX or inhibition of cytochrome P450 have also been explored. HO-1, Haem oxygenase 1; HO-2, Haem oxygenase 2; COHb, CO-haemoglobin complex; sGC, Soluble guanylyl cyclase; cGMP, Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; COX, Cyclo-oxygenase.
