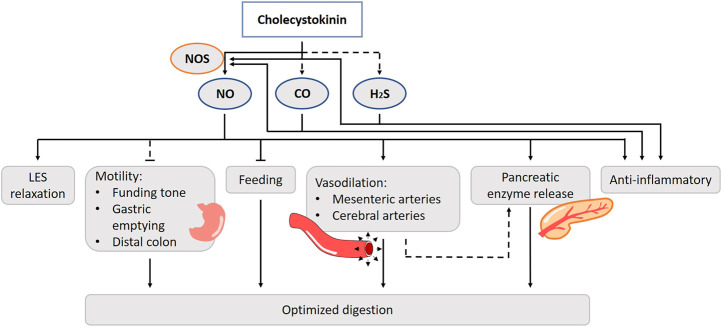
FIGURE 5.
Role of gasotransmitters on cholecystokinin’s (CCK) physiological functions. Solid lines are clear evidence–based on blockers and substrate administration. Dotted lines represent first evidence for the presence of the pathway. CCK stimulates nNOS activity and thus NO release. NO is involved in the cholecystokinin effect on LES relaxation, intestinal vasodilation and food intake regulation. The CCK-NO-pathway of intestinal motility has only been hypothesized in literature. CCK anti-inflammatory actions are evoked by reducing vascular and macrophage iNOS-derived NO production. The involvement of CO and H2S in these functions have only been suggested, but lack experimental prove. NO, Nitric oxide; CO, Carbon monoxide; H2S, Hydrogen sulfide; NOS, Nitric oxide synthase; LES, Lower esophageal sphincter.