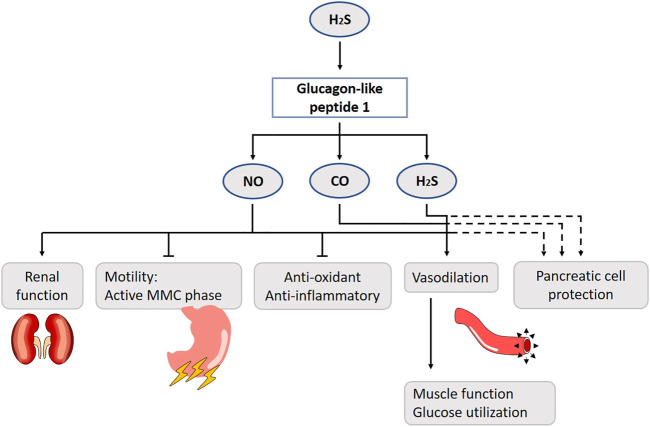
FIGURE 9.
Role of gasotransmitters on glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) release and its physiological functions. Solid lines are clear evidence–based on blockers and substrate administration. Dotted lines represent first evidence for the presence of the pathway. H2S stimulates GLP-1 release. The suppression of gut motility, reduction of nephropathy risk factors, increase of muscle microvasculature, reduction of the number of reactive oxygen species and production of vasoconstrictive mediators are GLP-1 effects mediated by NO. H2S and CO also contribute to the vasodilation. It has been suggested that the gasotransmitters play a protective role to govern pancreatic function in case of glucotoxicity. NO, Nitric oxide; CO, Carbon monoxide; H2S, Hydrogen sulfide; MMC, Migrating motor complex.