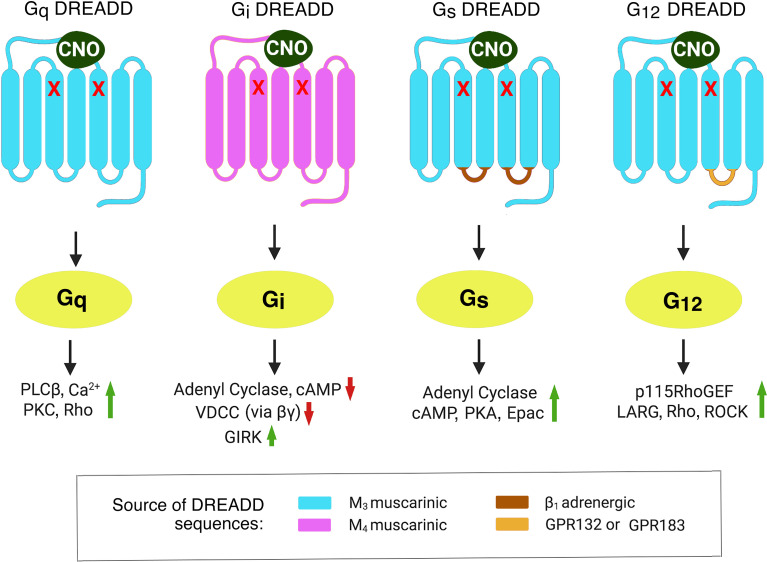
Figure 1.
Structural properties of DREADDs able to selectively activate each of the four major subclasses of heterotrimeric G proteins. The DREADDs shown here are all mutant muscarinic acetylcholine receptors that can be activated by CNO with high potency and efficacy. The red x marks indicate point mutations that prevent acetylcholine from activating these designer receptors (5). The Gq and Gi DREADDs were developed by Armbruster et al. (5). The Gs and G12 DREADDs were generated in the laboratories of Jürgen Wess (6) and Asuka Inoue (7), respectively. Activated G protein α-subunits stimulate or inhibit distinct intracellular effector enzymes or ion channels. This figure represents a modified version of Figure 1 published in (8). Epac, exchange protein activated by cAMP; GIRK, G-protein-regulated inward-rectifier potassium channel; LARG, Leukemia-Associated RhoGEF; PLCβ, phospholipase Cβ; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; RhoGEF, Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor; ROCK, Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase; VDCC, voltage-dependent Ca2+-channel.