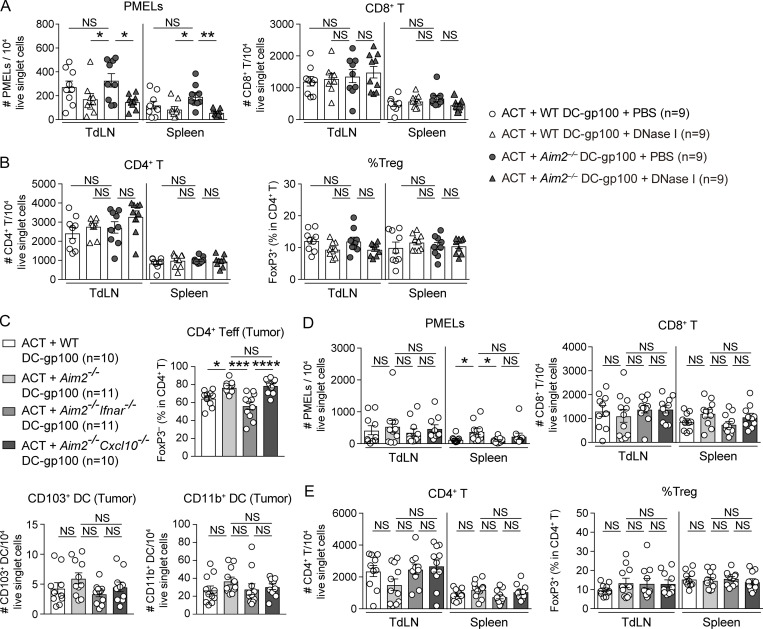
Figure S3.
The role of DNA sensing, IFNAR, and CXCL10 in AIM2-deficient DC vaccine with ACT on tumor, TdLN, and spleen in the B16F10 model.(A and B) Flow cytometry analysis of the numbers of PMELs, CD8+ T cells (A), and CD4+ T cells among 104 live singlet cells and percentages of FoxP3+ cells in CD4+ T cells (B) in the TdLN and spleen of B16F10 mice treated with ACT + WT or Aim2−/− DC-gp100 and intratumoral administration of DNase I or PBS (n = 9). (C–E) Flow cytometry analysis of the percentage of FoxP3− cells in total CD4+ T cells, numbers of CD103+ and CD11b+ DCs among 104 live singlet cells in the tumor (C), numbers of PMELs, CD8+ T cells (D), and CD4+ T cells among 104 live singlet cells and percentages of FoxP3+ cells in CD4+ T cells (E) in the TdLN and spleen of B16F10 mice treated with ACT + WT, Aim2−/−, Aim2−/−Ifnar−/−, or Aim2−/−Cxcl10−/− DC-gp100 (n = 10 or 11). Data are shown as mean ± SEM and are pooled from four (A and B) or three (C–E) independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test (A–E).