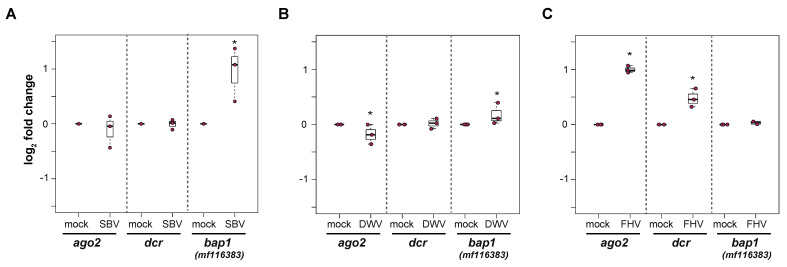
Figure 7.
Virus infections of primary honey bee pupal cells differentially impact the expression of select immune genes. The relative expression of three honey bee immune genes, argonaute-2 (ago2), dicer-like (dcr-like), and bee antiviral protein-1 (bap1)/mf116383, were assessed by qPCR at 72 hpi. The ΔΔCt method with normalization to rpl8 was utilized to assess target gene expression in each sample, and then the log2 fold change values were calculated relative to mock-infected samples. Raw data are included in Supplemental Tables S9–S11. (A) SBV infection of pupal cells did not impact ago2 or dcr-like expression, whereas the expression of bap1 was 0.95 log2-fold greater at 72 hpi (p = 0.032). (B) DWV-infected pupal cells exhibited slightly lower ago2 expression (p = 0.032) relative to mock-infected cells at 72 hpi, whereas there was no impact of virus infection on dcr-like expression. The expression of bap1 was 0.18 log2-fold higher in DWV-infected pupal cells compared to mock-infected cells at 72 hpi (p = 0.032). (C) In pupal cells infected with FHV, ago2 and dcr-like expression was higher (i.e., 1 and 0.48 log2-fold change, respectively, p = 0.032) in FHV-infected cells relative to mock-infected cells at 72 hpi. The expression of bap1 was not impacted by FHV infection. The differences in log2 immune gene relative expression in infected cells relative to mock-infected (PBS-treated) cells at 72 hpi were assessed using a one-sided Wilcoxon Rank Sums test. Significance level: * p < 0.05.