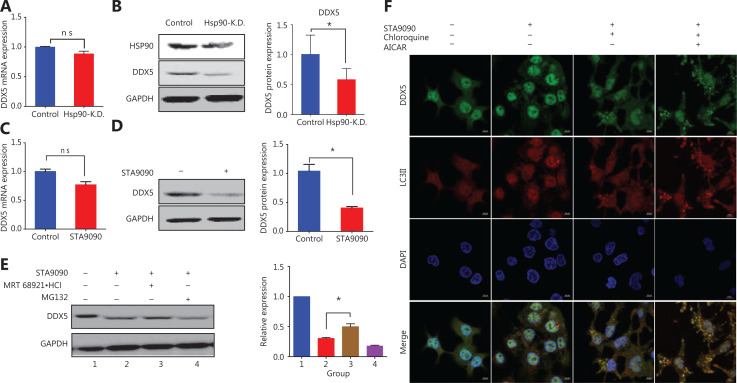
Figure 3.
HSP90 inhibits the autophagic degradation of DDX5 protein. (A) The mRNA level of DDX5 after HSP90 knockdown with shRNA (Hsp90-K.D.), tested by qRT-PCR, using GAPDH as a reference gene. (B) The protein level of DDX5 after HSP90 knockdown (Hsp90-K.D.) (mean ± SD, *P = 0.0238). (C) The mRNA level of DDX5 after STA9090 treatment, tested by qRT-PCR, using GAPDH as a reference gene. (D) The protein level of DDX5 after STA9090 treatment (mean ± SD, *P = 0.0294). (E) The inhibitory effect of DDX5 expression in the presence of STA9090, an inhibitor of HSP90, was ameliorated in HepG2 cells treated with an inhibitor for autophagy, MRT68921, but not by MG132, an inhibitor of proteasomes. (F) Confocal microscopy of intracellular localization analysis of DDX5 and autophagosomes after treatment with STA9090, chloroquine, and AICAR (Scale bar: 10 μm). Chloroquine: inhibitor of lysosome; AICAR: agonist of autophagy. Arrow: DDX5 combined with autophagosomes.