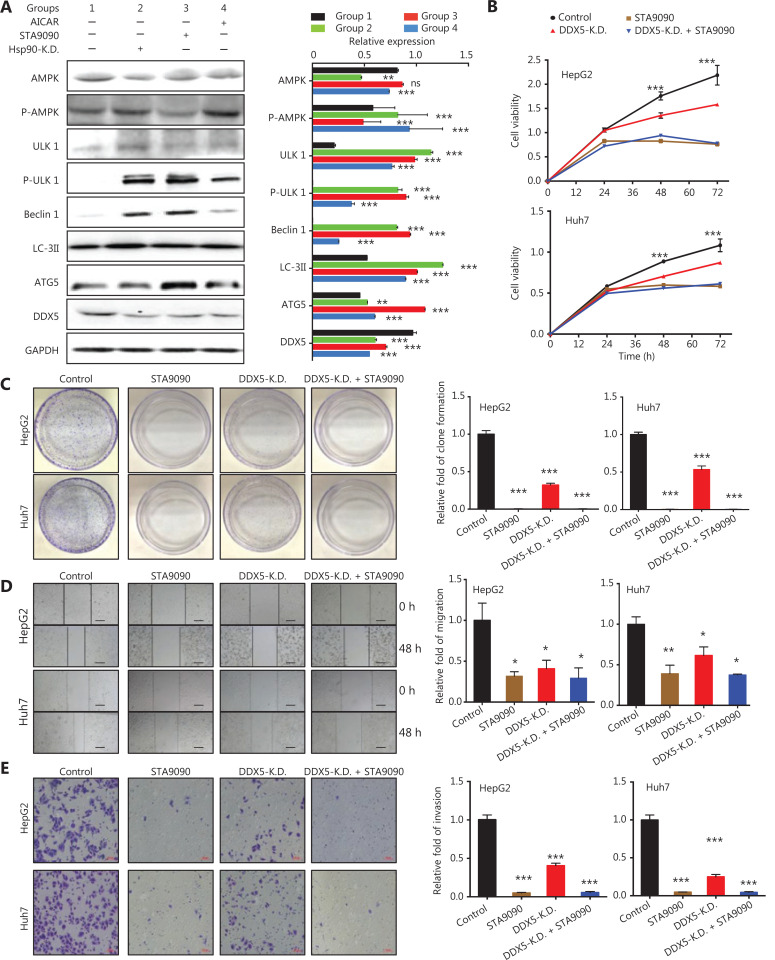
Figure 4.
HSP90 inhibits DDX5 degradation and increases its expression by inhibition of the AMPK/ULK1-regulated autophagic pathway. (A) Western blot analysis of the protein expressions of AMPK, p-AMPK, ULK1, p-ULK1, Beclin1, LC3II, ATG5, and DDX5 in HepG2 cells treated with AICAR (positive control) STA9090 (a HSP90 inhibitor), and HSP90 knockdown (Hsp90-K.D). (B–E) Inhibition of DDX5 decreases cellular viability, migration, and invasion in the hepatoma cell line. (B) The cell viability of both HepG2 and Huh7 cell lines determined by the CCK8 assay. Circle, control group; square, STA9090 treatment group; upper triangle, DDX5 knockdown group (DDX5-K.D.); down triangle, the group treated with both DDX5-K.D. and STA9090. (C) Lack of DDX5 (DDX5-K.D. or STA9090 treatment) inhibited cellular proliferation in both HepG2 and Huh7 cells. (D) Cellular migration (D) and invasion (E) was inhibited in both Huh7 and HepG2 cells in DDX5 KD or STA9090 treatment (Scale bars, 200 μm). Data are from a representative experiment that was repeated 3 times with similar results (mean ± SD, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).