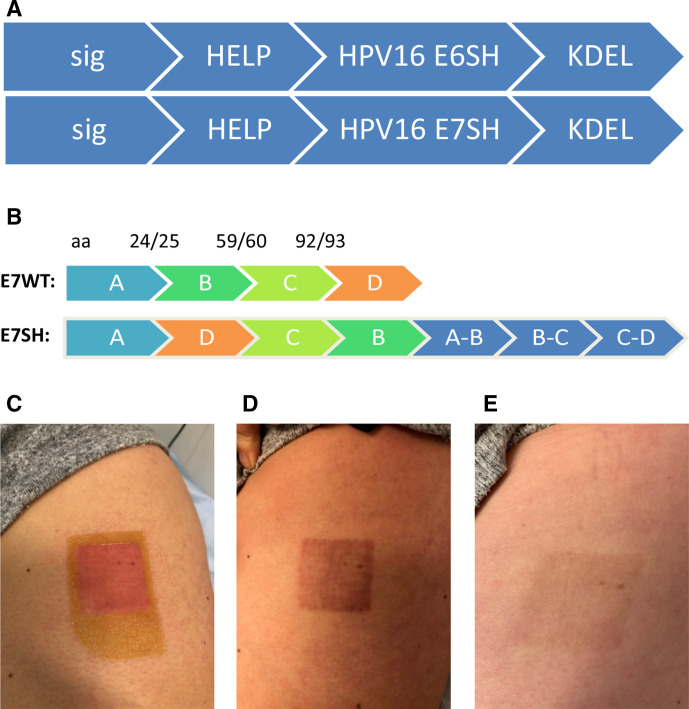
Figure 1.
pUMC3 sig-HELP-E6SH-KDEL and pUMVC3 sig-HELP-E7SH-KDEL plasmids used in this trial and administered by tattoo vaccination. (A) Schematic representation of the therapeutic region of the plasmid, including three helper sequences: synthetic epitope pan human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DR epitope (39 bp), negative factor from HIV (39 bp) and P30 from tetanus toxin (63 bp) for CD4 help. Sig and KDEL for improved endoplasmatic reticulumtargeting and retention, resulting in better antigen uptake by dentritic cellss, enhanced processing and presentation. (B) To prevent toxicity, E6 and E7 coding sequences were shuffled. Splice sites are added at the back of the construct so no potential immunogenic epitopes are lost. (C) Picture of the patients’ skin immediately after vaccination with human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 E6/E7 tattoo vaccination. (D) Picture of the skin 2 weeks after vaccination. (E) Picture of the skin 6 months after last vaccination, demonstrating hardly any visible tissue scar remains.