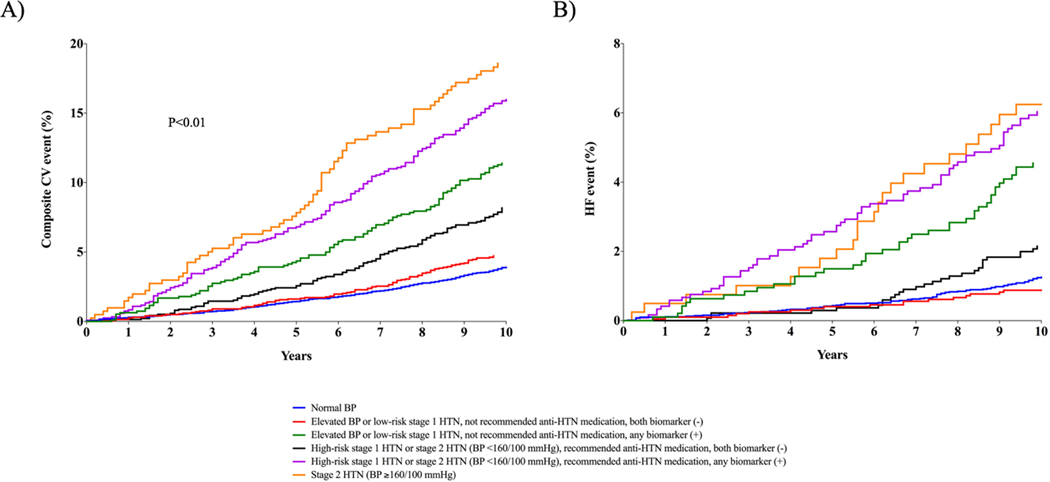
Figure 2. Cumulative incidence of composite CV event (ASCVD or HF, Panel A) and HF (Panel B) across 2017 ACC/AHA BP guideline recommended blood pressure treatment groups stratified by presence of elevated hs-cTnT or NT-proBNP.
Normal BP: <120/80 mm Hg; Elevated BP: 120–129/<80 mm Hg; stage 1 HTN: 130–139/80–89 mm Hg; stage 2 HTN: ≥140/90 mm Hg; high-risk stage 1 HTN was defined by the presence of any of the following: PCE-estimated 10-year ASCVD risk ≥10%, diabetes mellitus, estimated GFR <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, or age ≥65 years with systolic BP ≥130 mmHg; in the absence of all of these risk factors, individuals with stage 1 HTN were classified as low-risk; both biomarker (−): hs-cTnT <6 ng/L and NT-proBNP <100 pg/mL; any biomarker (+): hs-cTnT ≥6 ng/L and/or NT-proBNP ≥100 pg/mL; Composite CV event = non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke, HF, or CV death.
Abbreviations: anti-HTN= antihypertensive; ASCVD = atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BP = blood pressure; CV = cardiovascular; GFR = glomerular filtration rate; HF = heart failure; hs-cTnT = high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; HTN = hypertension; MI = myocardial infarction; NT-proBNP = N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; PCE = pooled cohort equation.