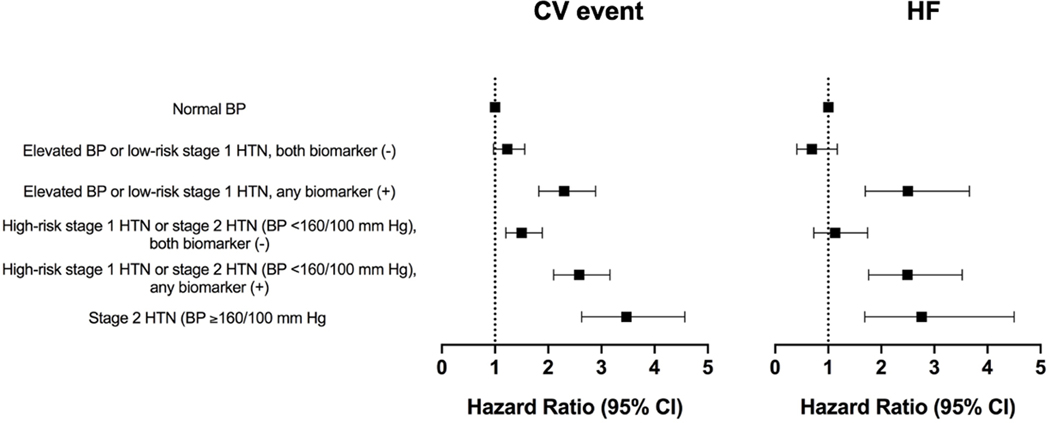
Figure 5: Multivariable adjusted association between the 2017 ACC/AHA BP guideline recommended treatment groups stratified by biomarker status and incident composite CV event (ASCVD or HF) and HF.
Multivariable adjusted Cox models were constructed to evaluate the association between the BP/biomarker-based study groups and risk of outcome [composite CV event (non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke, HF, or CV death) or HF (referent group = normal BP)] with adjustment for the following potential confounders: demographics (age, sex, race), CV risk factors (BMI, diabetes mellitus status, smoking status), laboratory values (total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, estimated glomerular filtration rate), medications (statin use), and study cohort. Elevated BP: 120–129/<80 mm Hg; stage 1 HTN: 130–139/80–89 mm Hg; stage 2 HTN: ≥140/90 mm Hg; high-risk stage 1 HTN was defined by the presence of any of the following: PCE-estimated 10-year ASCVD risk ≥10%, diabetes mellitus, estimated GFR <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, or age ≥65 years with systolic BP ≥130 mmHg; in the absence of all of these risk factors, individuals with stage 1 HTN were classified as low-risk; any biomarker (+): hs-cTnT ≥6 ng/L and/or NT-proBNP ≥100 pg/mL.
Abbreviations: ASCVD = atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BMI: body mass index; BP = blood pressure; CV = cardiovascular; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; HDL: high density lipoprotein; HF = heart failure; hs-cTnT = high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; HTN = hypertension; MI = myocardial infarction; NT-proBNP = N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; PCE: pooled cohort equation.