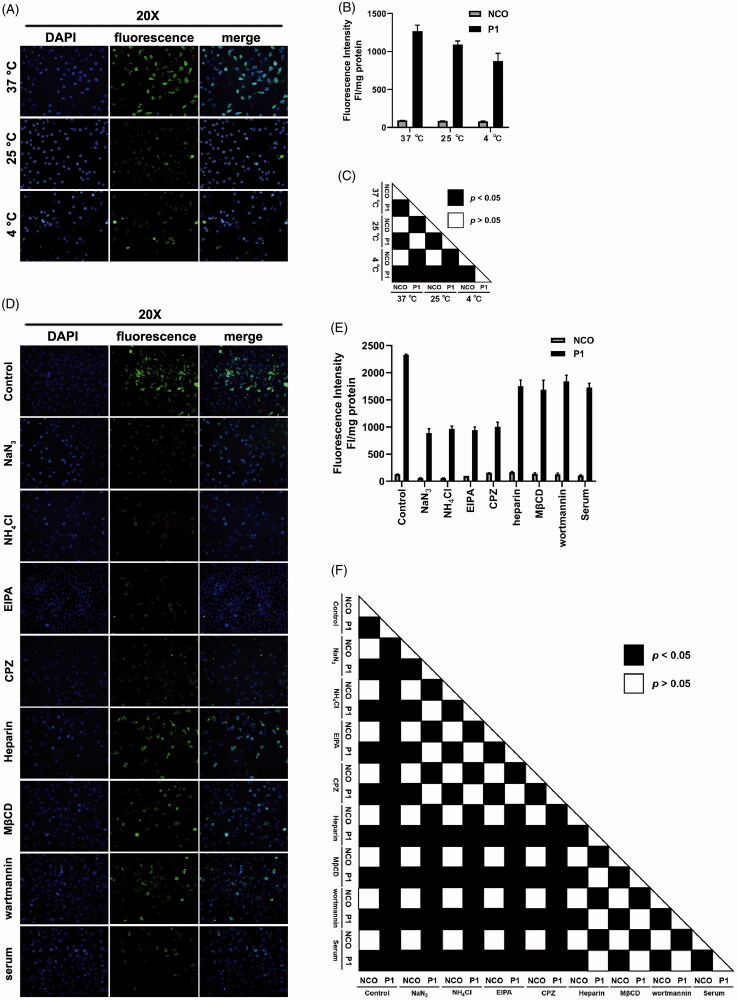
Figure 5.
Mechanisms involved in peptide P1 penetration. (A) Fluorescence microscopy images of peptide P1 (5 μM) incubated at different temperatures. (B) Quantification of fluorescent intensity of peptide P1 (5 μM) incubated at different temperatures. The fluorescence of the cellular uptake was normalized by cellular protein. Values represent mean ± SEM. (C) The corresponding p-value plot between data pairs presenting in (B). ANOVA was used to compare the differences between the control and experimental values. (D) Fluorescence microscopy images of peptide P1 (5 μM) incubated with different endocytosis inhibitors. (E) Quantification of fluorescent intensity of peptide P1 (5 μM) incubated with different endocytosis inhibitors. The fluorescence of the cellular uptake was normalized by cellular protein. Values represent mean ± SEM. (F) The corresponding p-value plot between data pairs presenting in (E). ANOVA was used to compare the differences between the control and experimental values.